What is Glycolysis? – Definition, Stages, Diagram
All plants in an ecosystem produce food through the Photosynthesis process, however, in order to convert the produced food into energy the Glycolysis process plays a very important role. And here in the below article, we will help you understand all about the Glycolysis Cycle, and all the different stages involved in this process in much more detail.
What is Glycolysis?
The glycolysis process is defined as, a metabolic procedure that involves converting glucose into pyruvic acid. In other words, through this process, glucose is broken down to produce energy. Moreover, this process is commonly found in the cytoplasm of the cell, it generally results in the formation of pyruvate, water, NADH, and ATP. Besides, unlike other processes, this does not have any oxygen, and it is actively observed in aerobic as well as anaerobic organisms.
Glycolysis Diagram
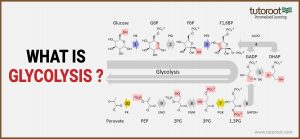
The above diagram explains cellular respiration, and how the quantities are converted throughout this process. And here in this section, we will talk about the different stages of the Glycolysis reaction, that are described above.
Stage 1
In this stage, the glucose is trapped inside a cell, by the addition of phosphate group to glucose, because of the enzyme hexokinase. Moreover, the addition of this phosphate group to glucose results in the formation of 6-phosphate.
Stage 2
Now in this stage, because of the enzyme phosphoglucomutase, Glucose 6-phosphate undergoes isomerization into forming fructose 6-phosphate.
Stage 3
The ATP Molecule inside the cell results in the transfer of phosphate molecule to fructose 6-phosphate, which results in the formation of fructose 1,6-biphosphate, because of the enzyme phosphofructokinase.
Stage 4
For this stage, the enzyme aldolase plays a major role in converting or forming isomers such as glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, and dihydroxyacetone phosphate, by converting the fructose 1,6-biphosphate.
Stage 5
Triose-phosphate isomers play an active role and convert dihydroxyacetone phosphate into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
Stage 6
Unlike other stages, this one involves two reactions,
-
- The first reaction results in the formation of NADH +H+, by transferring one hydrogen molecule from glyceraldehyde phosphate to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. This process is possible because of the enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
- Now the above-mentioned enzyme adds another phosphate to the oxidized glyceraldehyde phosphate, which will result in 1,3 biphosphoglycerate.
Stage 7
Next, in stage 7, the phosphate from 1,3 biphosphoglycerate to ADP to ATP, with the assistance of the enzyme, phosphoglycerokinase. Moreover, this stage will result in two molecules of ATP and Phosphoglycerate.
Stage 8
The two phosphoglycerate molecules will lose two phosphates from the third carbon to the second carbon, mainly by yielding two molecules of 2-phosphoglycerate with the help of the enzyme phosphoglyceromutase.
Stage 9
Now the water molecule, from the 2-phosphoglycerate, is removed, which will lead to the formation of phosphoenolpyruvate, with the enzyme enolase.
Stage 10
Through the enzyme pyruvate kinase, the phosphate from phosphoenolpyruvate gets transferred to ADP and will result in forming ATP and pyruvate.
Highlights of Glycolysis Cycle
Besides, Glycolysis Reaction has various important highlights, which we must keep in mind, such as,
- As you know through this process, the glucose mole is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate.
- Besides, through the Glycolysis reaction, the end products formed are 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 ADP, and 2 NADH molecules.
- Moreover, as you can observe six different types of enzymes take part in different stages of the Glycolysis cycle.
- Furthermore, the Glycolysis reaction is observed in both cytoplasms of animal and plant cells.
Conclusion
From the above article, as you can see, these reactions are very complex, and so generally hard to understand. And in this subject, you will find many more complex topics and reactions. Because of this, we suggest you join the online interactive classes offered by the Tutoroot platform. Through this online coaching program, the students can access various benefits, like Doubt Clearing Sessions, Best Educational Materials, Expert Staff Guidance, Cost Effective Prices, and a lot more.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the end product of glycolysis?
The Glycolysis process results in the end products such as ATP, NADH, ADP, and Pyruvate.
