Complete Guide of the Human Brain – Structure, Function
Introduction to the Human Brain
The human brain is a remarkable organ, often considered the command center of the body. It controls everything from our thoughts and emotions to bodily functions like breathing and digestion. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the structure and function of the human brain, providing you with a clear understanding of this complex organ.
The human brain is an incredibly intricate and essential part of our body. It is responsible for processing information, regulating various bodily functions, and giving rise to our thoughts, feelings, and consciousness. To better understand the brain, we’ll start by looking at a human brain diagram, which will give us a visual overview of its structure.
Human Brain Diagram
Before diving into the detailed explanations, let’s take a moment to explore a simplified human brain diagram. The brain can be divided into three major sections: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain.
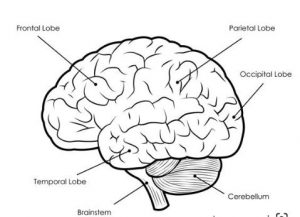
Now, let’s break down each of these sections.
Forebrain
The forebrain is the largest part of the brain and plays a crucial role in higher-order thinking, such as problem-solving, decision-making, and emotional regulation. It includes several important components:
- Cerebrum: This is the largest part of the forebrain and is responsible for thinking, memory, reasoning, and processing sensory information.
- Thalamus: The thalamus acts as a relay station for sensory information, routing it to the appropriate parts of the cerebrum for processing.
- Hypothalamus: The hypothalamus controls various bodily functions like hunger, thirst, body temperature, and even emotions.
Midbrain
The midbrain is a relatively small part of the brain that primarily deals with sensory and motor functions. It includes:
- Tectum: The tectum is responsible for controlling certain reflexes, such as eye movements in response to visual stimuli.
- Tegmentum: The tegmentum plays a role in motor coordination and contains structures involved in the sensation of pain.
Hindbrain
The hindbrain is located at the back of the brain and is involved in essential functions like balance, coordination, and the regulation of involuntary activities. It consists of the following parts:
- Cerebellum: The cerebellum is responsible for coordinating voluntary muscle movements and maintaining balance and posture.
- Pons: The pons serve as a bridge between different parts of the brain and play a role in functions like sleep and facial movements.
- Medulla Oblongata: The medulla oblongata controls vital functions like breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the brain’s major sections, let’s delve deeper into the individual parts of the human brain and their functions.
Human Brain Parts and Their Functions
Cerebrum
The cerebrum, the brain’s largest component, is divided into two hemispheres: the left and the right. Each hemisphere is responsible for governing the contralateral (opposite) side of the body. Moreover, the cerebrum is subdivided into four lobes, each with distinct functions:
- Frontal Lobe: This lobe is responsible for reasoning, problem-solving, emotions, and motor function.
- Parietal Lobe: The parietal lobe processes sensory information from the body, such as touch and temperature.
- Temporal Lobe: The temporal lobe is engaged in memory, auditory perception, and comprehension of language.
- Occipital Lobe: The occipital lobe is chiefly accountable for the interpretation of visual information.
Importance: The cerebrum is essential for our ability to reason, learn, communicate, and interact with the world. It is the seat of human consciousness and is vital for complex intellectual and motor tasks.
Thalamus
The thalamus is a small, egg-shaped structure deep within the brain.
- Functions: It acts as the brain’s information junction, receiving sensory information from various parts of the body and routing it to the appropriate sections of the cerebral cortex. It plays a crucial role in relaying sensory signals like vision, hearing, taste, and touch to the brain.
- Importance: The thalamus is vital for processing and directing sensory information to higher brain regions, enabling us to perceive and respond to our environment.
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus plays a critical role in maintaining the body’s internal balance, or homeostasis. The hypothalamus is a tiny but powerful region located just below the thalamus.
- Functions: It regulates many essential bodily functions, including body temperature, hunger, thirst, and the sleep-wake cycle. The hypothalamus also controls the release of hormones from the pituitary gland, affecting various physiological processes.
- Importance: The hypothalamus is crucial for maintaining internal balance and homeostasis, ensuring our body functions properly and responds to changing external and internal conditions.
Cerebellum
The cerebellum is located at the back of the brain and is often referred to as the “little brain.”
- Functions: Its main function is to coordinate voluntary muscle movements, maintain balance, and regulate posture. It fine-tunes motor skills and helps in activities like walking, dancing, and playing musical instruments.
- Importance: The cerebellum is crucial for smooth, precise movements and ensuring that we can perform activities with grace and accuracy. It plays a fundamental role in our ability to move and interact with our environment.
Pons
The pons serve as a bridge between different parts of the brain, transmitting signals between the cerebrum and the cerebellum. It plays a role in sleep and is responsible for various facial movements.
Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata oversees critical functions necessary for survival, including the regulation of respiration, heart rate, and blood pressure.
Amygdala
The amygdala is a small, almond-shaped cluster of nuclei located within the temporal lobe of the brain.
- Functions: It plays a central role in processing and regulating emotions, particularly those related to fear and pleasure. The amygdala is involved in emotional memory, decision-making, and the detection of threats.
- Importance: The amygdala is essential for our emotional experiences, helping us respond to and navigate potentially dangerous or rewarding situations.
Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a seahorse-shaped structure located within the temporal lobes.
- Functions: It is primarily responsible for memory formation, consolidation, and spatial navigation. The hippocampus is crucial for creating and storing both short-term and long-term memories.
- Importance: Without the hippocampus, we would have difficulty forming new memories and recalling past experiences. It is a key player in our ability to learn and remember.
Corpus Callosum
The corpus callosum is a thick bundle of nerve fibers that connects the two hemispheres of the brain.
- Functions: It serves as the brain’s internal communication system, allowing information to flow between the left and right hemispheres. It facilitates coordination between the two hemispheres for tasks that require input from both sides.
- Importance: The corpus callosum enables the integration of information and coordination of functions between the brain’s hemispheres, which is critical for various complex cognitive tasks, problem-solving, and sensory processing.
Brainstem
The brainstem is the lower part of the brain that connects to the spinal cord and includes the midbrain, pons, and medulla.
- Functions: It oversees automatic functions that are essential for survival, such as regulating breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and basic reflexes like swallowing and sneezing.
- Importance: The brainstem is responsible for maintaining vital bodily functions, and damage to this area can be life-threatening. It acts as the control center for many of our body’s automatic processes.
Functionality of the Human Brain
The human brain is a complex and dynamic organ with various functions that are essential for our daily lives. Here are some key functions of the human brain:
- Thinking and Reasoning: The cerebrum is responsible for higher-order thinking processes, enabling us to solve problems, make decisions, and engage in complex reasoning.
- Memory: The brain stores and retrieves information, allowing us to remember facts, experiences, and skills.
- Sensory Processing: Different parts of the brain process sensory information, helping us perceive and respond to our environment.
- Emotion Regulation: The brain, especially the limbic system, plays a crucial role in controlling our emotions.
- Motor Control: The cerebellum and various brain regions coordinate our voluntary muscle movements, ensuring our actions are precise and coordinated.
- Homeostasis: The hypothalamus helps maintain our internal balance by regulating hunger, thirst, body temperature, and sleep patterns.
- Autonomic Functions: The medulla oblongata controls involuntary functions like breathing and heart rate, crucial for our survival.
Location of the Human Brain
The human brain is situated within the skull, encased in protective bone. It is located at the top of the spinal cord and is connected to the rest of the body through a network of nerves. This central position allows the brain to communicate with and control various bodily functions.
Final Verdict
The human brain is a marvel of nature, with its intricate structure and diverse functions. It is responsible for our thoughts, emotions, and bodily functions, making it one of the most vital organs in our body. Understanding the various parts of the brain and their functions is not only fascinating but can also help us appreciate the incredible complexity of the human mind.
In conclusion, the human brain is a remarkable and complex organ that controls our thoughts, emotions, and bodily functions. By exploring its structure and functions, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of this vital organ.
For more simplified explanations like the one above, visit the biology blogs on the Tutoroot website. Elevate your learning with Tutoroot’s personalised Biology online tuition classes. Begin your journey with a FREE DEMO session and discover the advantages of one-on-one online guidance.
We trust that this article aids your comprehension of the Human brain along with human brain functions and its diagram. If you’re in search of top-notch online tutoring services, feel free to explore Tutoroot. Click here to schedule a FREE DEMO with some of the finest educators in the industry.
FAQs
What is the weight of the human brain?
The weight of the human brain varies from person to person, but on average, it is approximately 3 pounds (1.4 kilograms).
How many neurons are in the human brain?
The human brain contains around 86 billion neurons. These are the cells that transmit information and allow us to think, feel, and interact with the world.
How many brain cells does a human have?
In addition to the 86 billion neurons, the human brain also contains various other types of cells, including glial cells, which support and protect neurons. The total number of cells in the human brain is estimated to be in the trillions.
Understanding the human brain’s structure and function is a fascinating journey that can lead to a deeper appreciation of the remarkable capabilities of this organ. Whether you’re an 8th-grade student or just someone curious about the brain, this guide provides a solid foundation for your exploration of this complex subject.
