What are Longitudinal and Transverse Waves? – Difference, Diagram
Introduction
Welcome to this article where we dive into the fascinating world of waves! Whether it’s the sound of your favorite song reaching your ears or the sight of ocean waves crashing onto the shore, waves are all around us. In order to understand the concept of waves better, we need to explore the two main types: longitudinal waves and transverse waves. So, let’s embark on this journey together and unravel the differences between them with detailed explanations and diagrams.
What is a Wave?
Before we delve into the specifics of longitudinal and transverse waves, let’s first understand what a wave is. In simple terms, a wave can be defined as a disturbance that travels through a medium. This disturbance carries energy from one point to another, without any transfer of matter. Visualize a pebble being thrown into a still pond, causing ripples to spread outward. These ripples represent waves, with each point in the water moving up and down or side to side as the wave passes through.
Types of Waves
Now that we have a basic understanding of what waves are, let’s explore the two major types: longitudinal waves and transverse waves. These classifications occur based on the direction in which the particles of the medium oscillate as the wave propagates through it.
What is a Longitudinal Wave?
A longitudinal wave is characterized by particle oscillation occurring parallel to the direction of wave propagation. In simpler terms, if you imagine a slinky toy, where the coils represent particles of the medium, a longitudinal wave will result in compression and rarefaction of the coils in the same direction as the wave is moving. This leads to a back-and-forth motion of particles along the same axis as the wave’s propagation.
To better understand this, let’s take the example of sound waves. When someone speaks, the sound waves they produce are longitudinal. As the speaker’s vocal cords vibrate, they create compressions and rarefactions in the surrounding air particles. These vibrations then travel through the air, transmitting the sound waves to our ears.
Examples of Longitudinal Waves
Apart from sound waves, several other phenomena exhibit longitudinal wave characteristics. The following are a few examples of longitudinal waves.
- One example is a seismic wave, which occurs during an earthquake. The vibrations from the earthquake led to the compression and rarefaction of particles in the ground, creating longitudinal waves that propagate through the Earth’s layers.
- Similarly, ultrasound waves used in medical procedures also fall under the category of longitudinal waves.
- Also, sound waves are classic examples of longitudinal waves. The vibrations from a sound source, like a speaker or a guitar string, create compressions and rarefactions in the air, resulting in the transmission of sound.
What are Transverse Waves?
In contrast to longitudinal waves, transverse waves exhibit particle oscillation perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. Picture a wave on a string, where you create a disturbance by moving your hand up and down. The resulting wave would cause the string to move in a perpendicular direction to the original motion. This perpendicular motion of the particles defines a transverse wave.
An example of a transverse wave can be observed in electromagnetic waves, such as light. As light travels, the electric and magnetic fields oscillate perpendicular to the direction in which the wave is moving. This leads to the characteristic properties of light, like polarization, which are a direct consequence of the transverse nature of the wave.
Examples of Transverse Waves
Here are a few examples of transverse waves. Transverse waves can be observed in various natural phenomena.
- When you see waves in the ocean, those are transverse waves. The motion of water molecules occurs perpendicular to the direction in which the waves travel.
- Additionally, waves on a guitar string or any other instrument string are also examples of transverse waves. As the strings vibrate, they create waves that propagate through the air, producing the sound we hear.
- When you turn on a flashlight, light waves travel transversely. The electric and magnetic fields oscillate perpendicular to the direction of the wave. Hence light waves are also the best example of transverse waves.
Longitudinal and Transverse Wave Diagrams
To further enhance our understanding, let’s visualize longitudinal and transverse waves through diagrams. By providing a visual representation, we can grasp the concepts more easily. For the sake of simplicity, let’s consider a one-dimensional diagram that shows the direction of particle oscillation as well as the wave propagation.
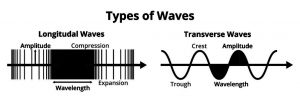
As depicted in the diagram, the longitudinal wave showcases particles moving back and forth in the same direction of the wave’s propagation. On the other hand, the transverse wave displays particles oscillating up and down perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. These diagrams provide a clear distinction between the two types of waves, aiding in their differentiation.
Difference Between Longitudinal Wave and Transverse Wave
The key differences between Longitudinal and Transverse Waves have been given below.
| Characteristic | Longitudinal Wave | Transverse Wave |
| Direction of Particle Movement | Parallel to the Wave Direction | Perpendicular to the Wave Direction |
| Example | Sound Waves | Light Waves, Radio Waves |
| Motion of Particles | Back-and-Forth | Up-and-Down |
| Crest and Trough | Compression and Rarefaction | Crest and Trough |
| Medium | Solid, Liquid, Gas | Usually Solid or Liquid (e.g., rope) |
Final Notes
In conclusion, waves play a significant role in our daily lives, whether we realize it or not. Understanding the characteristics and differences between longitudinal and transverse waves helps us comprehend the essence of various natural phenomena and artificial systems. So next time you hear a beautiful melody or witness waves crashing on the shore, take a moment to appreciate the remarkable world of waves and the secrets they hold.
Keen to easily grasp concepts, just as explained earlier? Explore our Tutoroot Blog for simplified learning. Deepen your understanding of subjects and get your questions answered with Tutoroot’s online tutoring. Experience Tutoroot’s physics online home tuitions now by scheduling a FREE DEMO session.
FAQs
Q: Why is a sound wave called a longitudinal wave?
A: Sound waves are called longitudinal waves because the motion of particles in the medium occurs in the same direction as the wave’s propagation. As a result, there are regions of compression and rarefaction that give rise to the characteristic properties of sound.
Q: Define longitudinal wave.
A: A longitudinal wave can be defined as a type of wave in which the particles of the medium oscillate parallel to the direction of wave propagation. This oscillation creates regions of compression and rarefaction as the wave travels through the medium.
