What are Osmosis and Diffusion? Definition, Diagram, and Differences
Cells are surrounded by a water solution containing nutrients, wastes, gases, salts, and other things. This is a cell’s exterior environment. The plasma membrane on the cell’s outer surface is in touch with the external environment, whereas the inner surface is in contact with the cytoplasm. As a result, the plasma membrane regulates what enters and exits the cell.
Some materials can pass through the membrane, but not all. The cell membrane is selectively permeable. Small compounds, for example, have the potential to penetrate across the membrane. When no energy is necessary for chemicals to move over a membrane, this is referred to as passive transport. In this article, we will look at two types of passive transport: diffusion and osmosis.

What is Osmosis?
Osmosis is a passive process that takes place without the need for any energy. It entails moving molecules from an area of greater concentration to a region of lower concentration until the concentrations on both sides of the membrane are equal.
Any solvent, including gases and supercritical liquids, can undergo osmosis.
Osmosis Diagram
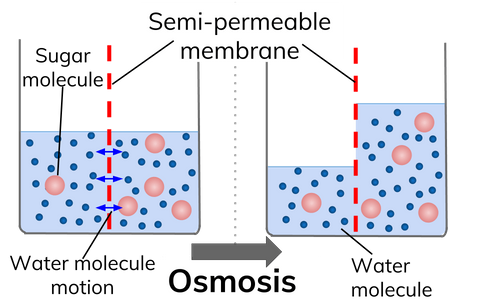
Types of Osmosis
There are two kinds of osmosis:
- Endosmosis: It occurs when a material is immersed in a hypotonic solution, and the solvent molecules travel into the cell, causing the cell to become turgid or undergo deplasmolysis. This is referred to as endosmosis.
- Exosmosis: Exosmosis occurs when a substance is submerged in a hypertonic solution and the solvent molecules escape, causing the cell to become flaccid or experience plasmolysis. This is referred to as exosmosis.
Osmosis Process
Osmosis is transporting a solvent through a semipermeable membrane that separates two solutions with different solute concentrations. During the process, the solvent moves from the lower solute concentration solution to the higher one.
Osmotic Pressure
Osmotic pressure is to prevent water from diffusing through a membrane due to osmosis. The concentration of the solute determines it. Water diffuses from the area with the lowest concentration to the area with the highest concentration. When the concentrations of the compounds in the two regions of contact differ, the substances disperse until the concentrations are uniform throughout.
Here is the formula to calculate osmotic pressure:
\(\Pi =MRT\)
where Π represents osmotic pressure, and
M denotes the solute’s molar concentration.
R denotes the gas constant.
The letter T stands for temperature.
Significance of Osmosis
- Osmosis regulates nutrition delivery and metabolic waste product release.
- Its job is to take water from the ground and transmit it to the plant’s upper portions through the xylem.
- It maintains the equilibrium of water and intercellular fluid levels in a live organism’s interior environment.
- It preserves the turgidity of cells.
- It is a method by which plants retain their water content in the face of continual water loss via transpiration.
- This mechanism regulates water transport from cell to cell.
- Osmosis causes cell turgor, which governs plant and plant component mobility.
- Fruit and sporangia dehiscence is also caused by osmosis.
- Higher osmotic pressure protects plants against drought damage.
What is Diffusion?
Diffusion is the motion of molecules over a concentration gradient. It is a key process that occurs in all living organisms. Diffusion facilitates the passage of chemicals into and out of cells. The molecules move from a high concentration zone to a low concentration zone until the concentration is uniform throughout.

Diffusion occurs in liquids and gases because molecules can flow randomly.
Types of Diffusion
Diffusion is widely employed in many domains, including biology, physics, and chemistry. There are two forms of diffusion:
Simple diffusion
A method of moving a chemical through a semipermeable barrier or a solution without the assistance of transport proteins. Bacteria, for example, transfer tiny nutrients, water, and oxygen into the cytoplasm by simple diffusion.
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the passive transport of molecules across the cell membrane from a high-concentration area to a low-concentration region by a carrier molecule.
- Dialysis: Dialysis is the process by which solutes diffuse over a selectively permeable membrane. A selectively permeable membrane permits just some ions and molecules to flow through while blocking the passage of others.
- Osmosis: Osmosis is the transport of solvent molecules from a low-concentration area to a high-concentration region across a semipermeable membrane. Because water is a solvent in all living things, scientists describe osmosis as water diffusion through a selectively permeable membrane. Plants, for example, use osmosis to extract water and nutrients from their roots.
Process of Diffusion
Diffusion is a natural and physical phenomenon that occurs without the need for stirring or shaking the solutions. Diffusion occurs in liquids and gases because molecules can flow randomly. The molecules clash, causing them to shift direction.
Significance of Diffusion
- This mechanism aids in the diffusion of carbon dioxide gas out through the cell membrane into the blood during the respiration process.
- Diffusion happens in plant cells as well. Through root cells, the water from the soil enters all green plants.
- Diffusion is responsible for the transport of ions between neurons, which creates electrical charge.
Differences Between Diffusion and Osmosis
| Osmosis | Diffusion |
| It is only applicable to the liquid media. | It occurs in liquids, gases, and even solids. |
| A semipermeable membrane is required. | A semipermeable membrane is not required. |
| It is defined by the number of solute particles dissolved in the solvent. | The existence of other particles influences it. |
| Water is required for particle mobility. | Water is not required for particle mobility. |
| Diffusion is limited to solvent molecules. | Solute and solvent molecules can both diffuse. |
| Particles can only flow in one direction. | Particle flow occurs in all directions. |
| An application of additional pressure to the solution side can stop or reverse the process. | This procedure cannot be stopped or reversed. |
| Only occurs between solutions of comparable kinds. | It occurs between solutions that are similar and solutions that are different. |
| It just includes the transfer of solvent molecules from one side to the other. | It entails moving all the particles from one place to another. |
| Solvent concentrations do not equalize on both sides of the membrane. | The diffusion material’s concentration equalizes to fill the available area. |
| It is determined by the solute potential. | It is unaffected by solute potential, pressure potential, or water potential. |
| An area of high concentration flows into an area of low concentration only by passing through water or another solvent. | Any material travels from the high concentration zone to the low concentration zone. |
| Mineral and nutrient absorption is unrelated. | Nutrients and minerals are absorbed better with their help. |
Final Notes
Learn more about osmosis and diffusion, its definition, types, effects, and differences from Tutoroot by opting for a 1:1 class customized to your needs.
FAQs
What is Osmosis?
Osmosis is a passive process that takes place without the need for any energy. It entails moving molecules from an area of greater concentration to a region of lower concentration until the concentrations on both sides of the membrane are equal.
Any solvent, including gases and supercritical liquids, can undergo osmosis.
How do you calculate Osmosis?
Here is the formula to calculate osmotic pressure:
Π=MRT
where Π represents osmotic pressure, and
M denotes the solute’s molar concentration.
R denotes the gas constant.
The letter T stands for temperature.
What is Diffusion?
Diffusion is the motion of molecules over a concentration gradient. It is a key process that occurs in all living organisms. Diffusion facilitates the passage of chemicals into and out of cells. The molecules move from a high concentration zone to a low concentration zone until the concentration is uniform throughout.
What are the major differences between Osmosis and Diffusion?
Osmosis is only applicable to the liquid media while diffusion happens in liquids, gases, and even solids. Osmosis is defined by the number of solute particles dissolved in the solvent whereas diffusion is all about the existence of other particles influences it.
Osmosis occurs between solutions of comparable kinds, includes the transfer of solvent molecules from one side to the other. Diffusion occurs between solutions that are similar and solutions that are different and entails moving all the particles from one place to another.
