What is Cytoplasm? – Definition, Structure, Function
In a cell, the Cytoplasm is the most essential part as it performs various functions and offers multiple benefits to all the components located inside. If you want to learn more about this component of the cell, then you are in the right place. As here, in this article, we are going to provide a comprehensive description of the Cytoplasm structure, Cytoplasm function, and many more.
What is a Cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm is generally defined as the liquid that fills the cell, as it contains various cell components such as Ions, Macro Molecular Structures, Proteins, Organelles, Filaments, etc. while encompassing the cytosol. However, unlike the other liquids in the cells, the Cytoplasm is a glass-forming liquid. It is semifluid in nature and is typically an external substance to the nuclear membrane, and internal when it comes to the cellular membrane. For a protoplasm, it is a nonnuclear substance. In those cells that possess a nucleus, the cytoplasm holds the entire organelles that famously include mitochondria.
As we set our focus on the cytoplasm structure, we also try and connect with the cytoplasm functions, we clearly define how they differ based on both Eukaryotic as well as Prokaryotic cells. For instance, in eukaryotic cells, the cytoplasm contains all the components except the nucleus, while in prokaryotic cells, the cytoplasm contains the genetic material of the cell.
Structure of Cytoplasm
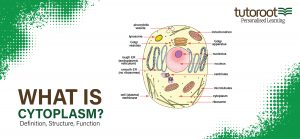
Now that we understand what a cytoplasm is, let us discuss in detail the structure of Cytoplasm. Firstly, as you already know, from the diagram of cytoplasm above you can find out that the cell generally consists of three main structures, Cytoplasm, Nucleus, and Plasma Membrane.
Coming back to cytoplasm structure, this, being an essential part of the cell, contains all the important components of the cell in its jelly-like structure adjoining the cell or plasma membrane as well as the nucleus. And more important processes in the cell, occur inside the cytoplasm.
As we know, cell organelles are those structures that are found inside the cells. These are clearly distinguished in their functions.
If we take the plasma membrane or cell membrane, it is a bi-lipid membranous layer, separating the cell organelles and the external environment and from various cells. This is also the external covering of a cell where parts like cytoplasm are covered.
We now come to the nucleus which is among the biggest of organelles and with special control on the cell. Finally, we arrive at the cytoplasm which is like jelly and in which the cell organelles are located.
Studying the cytoplasm structure vis-a-vis the cell, we realize that it is an essential component of the cell that is semi-liquid and jelly-like. Most importantly, it connects the nucleus and the cell membrane. Inside the cell, the cytoplasm looks embedded, while other cell organelles are loose and stay suspended within. Cytoplasm is where chemical reactions take place and the metabolism of a cell happens.
The cytoplasm structure is clearly explained in the cytoplasm diagram published in the article. Please refer to it for a better understanding through illustration.
Functions of Cytoplasm
Next in this article, we are going to talk about the different functions of the Cytoplasm such as,
- One of the most important functions of the Cytoplasm is maintaining the shape and structure of the cells in all types of organisms. Composed of salt and water, the cytoplasm is responsible for many cellular activities. it comprises molecules and enzymes that are important in waste breakdown.
Another important function of the Cytoplasm is the Transportation of organelles and other cellular components throughout the cell
As we know, a fundamental cytoplasm function is to maintain the shape and structure of the cell, it thus fills the cells up. In the absence of cytoplasm, the cells would be like those in deflated situation, and will spread from one organelle to another.
The cytoplasm also acts as a host to all the different metabolic processes or chemical reactions that occur in the cell.
Besides, the cytoplasm protects and stores all the components in the cell safely.
Protoplasm and how is it different from cytoplasm
While we now understand the cytoplasm structure and functions, it is also important to understand the structure of protoplasm. A protoplasm is the living part of the cell and is made up of macromolecules, water, and a synthesis of smaller molecules. It is colorless and is both inorganic and organic which comprises the cytoplasm, the nucleus, mitochondria, and the plastids of the cell. It is the most vital component of all the living processes. Cytoplasm structure clearly defines it as a primary and most integral part of protoplasm
Conclusion
In the above article, we helped you understand all about the Cytoplasm, its functions, Structures, and Cytoplasm Diagram. If you have any doubts regarding any other topics in this subject, then we would suggest you Join our exclusive interactive classes offered by Tutoroot, and get access to various benefits such as Special Doubt Clarification Sessions, Expert Staff Guidance, Access to Best Study Material or Guides, etc. Which in turn will help the students grasp a better knowledge of the subject, allowing them to rank high scores in the examinations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Cytoplasm definition
Cytoplasm is generally defined as the liquid that fills the cell, as it contains various cell components such as Ions, Macro Molecular Structures, Proteins, Organelles, Filaments, etc while encompassing the cytosol.
Is cytoplasm present in plant and animal cells?
Yes, Cytoplasm is available in both animals as well as plant cells.
What is major cytoplasm function in a plant cell?
As stated in the above sections of the article, the Cytoplasm performs various essential functions such as, holding components safely, protecting components from damage, hosting metabolic processes, transporting cellular components, etc.
What are the 4 functions of the cytoplasm?
- One of the most important functions of the Cytoplasm is maintaining the shape and structure of the cells in all types of organisms. Composed
- Another important function of the Cytoplasm is the Transportation of organelles and other cellular components throughout the cell
- The cytoplasm also acts as a host to all the different metabolic processes or chemical reactions that occur in the cell.
- Besides, the cytoplasm protects and stores all the components in the cell safely.
