What is Kingdom Fungi? – Classification, Diagram, Function
All the organisms that are omnipresent and consist of a cell wall, are classified as a species under the Kingdom Fungi. These organisms play a vital role in various important processes that support the growth and diversity of multiple species in an ecosystem. If you are new to this chapter, and you want to get more details about the Kingdom Fungi, then please go through the article below that will explain fungi classification with fungi diagram.
The article also throws light on the structure of fungi and the characteristics of fungi.
What is Kingdom Fungi?

Kingdom Fungi are defined as eukaryotic organisms, that are categorized as heterotrophs in the food chain, as they similar to other animals depend on autotrophs for food and energy. Besides, these types of organisms are generally observed in regions, where the atmosphere is warm and very moist. Some popular examples of fungi are mushrooms, yeasts Moulds, etc. it is important to delve deeper into the characteristics of fungi, besides the structure of fungi, in order to get a complete picture.
Structure of Kingdom Fungi
Now that you have a basic understanding of the Kingdom Fungi, let us now, discuss the fungi structure in a much more detailed fashion below, and also through the fungi diagram. This also gives a brighter picture of the fungi classification.
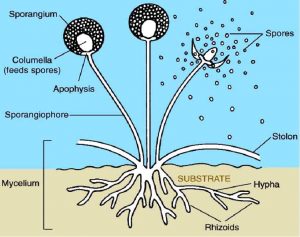
- Fungi can be either singular or multicellular organisms with similar structures.
- The filamentous structure is common for most fungi organisms except for yeast.
- Fungi structure consists of multiple components like cell organelles, cell walls, cytoplasm, nuclei, and cell membrane.
- Being a eukaryotic organism, it consists of a true nucleus that is surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
- The cell wall inside the fungi is made of protoplast.
- Besides, the fungi also consist of thread-like structures, called Hyphae, which combined together to form the structure mycelium.
Characteristics of Fungi
The characteristics of fungi can be as follows:
- The reproduction of fungi is made possible because of spores.
- The phenomenon of alternation of generation is a common trait of Fungi.
- Moreover, the reproduction process in fungi is not restricted, which means it can either be asexual or sexual based on the conditions.
- Furthermore, fungi have many parasitic subspecies, that are generally infectious and very harmful to their host.
- Unlike other eukaryotes, the nucleus observed in these species is very small in size.
- Similar to plants, fungi also store their food in the form of starch.
- However, due to the absence of pigment, chlorophyll, photosynthesis cannot occur in these organisms, so it cannot produce their own food.
- Popular examples of fungi are yeast, mushrooms, and Moulds.
Classification of Fungi
On the basis of various types, Kingdom Fungi are classified
Nutrition
As per the nutrition, kingdom fungi are categorized into three groups:
- Saprophytic fungi earn their nutrition by preying on dead organic substances
- Parasitic fungi that get their nutrition by relying on other living beings, both plants or animals, by grabbing the food from the host
- Symbiotic class of fungi that feature an interdependent alliance with fellow species with mutual gains. One of the popular examples is Lichens that feature the association of algae and fungi
Spore Formation Classification
Kingdom Fungi are classified as per spores:
- Zygomycetes, formed through the fusion of two cells
- Ascomycetes or sac fungi
- Basidiomycetes are the mushrooms that survive as parasites.
- Deuteromycetes or imperfect fungi are erratic and don’t stick to the conventional reproduction cycle like other fungi
Reproduction of Fungi
The Kingdom Fungi go through reproduction by sexual as well as asexual ways. The sexual mode is called teleomorph, whereas the asexual mode of reproduction is known as anamorph.
- Vegetative reproduction in fungi happens when there is budding, fission, and fragmentation.
- Fragmentation where certain forms under Ascomycotina and Basidiomycotina multiply with the breaking of the mycelium.
- Budding happens when certain unicelled forms multiply, and a bud sprouts as a papilla on the parent cell. Once it enlarges, it attains the stature of a single unit.
- Fission where unicelled forms multiply.
In the case of asexual reproduction, it happens through thin-walled spores named conidia zoospores, or sporangiospores. For the sexual type of reproduction, ascospores, basidiospores, and oospores play vital roles. In the case of sexual reproduction, the compatible nuclei exhibit a typical trait or behavior that leads to different phases of mycelia. The behaviors are thus classified as:
- Plasmogamy or two protoplasts’ fusion.
- Karyogamy or two nuclei’s fusion.
- Meiosis or reduction division.
It is interesting to note that the conventional sexual reproduction mode does not feature often in the case of kingdom Fungi.
Kingdom Fungi Summary
In summary, the typical characteristics of Kingdom Fungi broadly consist of the structural aspects where they are eukaryotic and non-vascular; content aspects, where the absence of chloroplast and photosynthesis form the major feature; behavioral aspects where fungi growth is slower in comparison with bacteria; and reproduction aspects such as spores, etc.
The characteristics of Kingdom Fungi can also be listed as per the plant body of fungi that is thallus. The cell walls of the Kingdom Fungi are made of chitin and cellulose and sometimes out of cellulose-glycogen, cellulose-chitin, or polygalactosamine-galactan.
Another important characteristic of Kingdom Fungi can be determined by their nutrition where the fungi are achlorophyllous cannot process food on their own, and are often seen as parasites or saprophytes.
Their reproductive aspects show that they happen in a vegetative fashion, and can be sexual or asexual.
Uses of Fungi
There are multiple uses that are mostly an inherent part of fungi structure. These can be:
- Fungi act as a source of food for multiple organisms in the ecosystem.
- Yeast, a form of fungi, is capable of producing Vitamin B. This is used to make various types of baking products like bread.
- Besides, food production, fungi also act as a decomposer.
- In addition to this, fungi also play an active role in the production of antibiotics such as Penicillin.
- Furthermore, fungi are actively used as a pesticide, in order to reduce or eliminate the insects and pests feeding on crops.
Conclusion
The above article will help you understand all about the Kingdom Fungi Classification, fungi structure, fungi reproduction, fungi characteristics as well as its various applications. And if you have doubts about any other similar topics or chapters in biology, then it would be a good idea for you to join the Online Home Tutor programs offered by the Tutoroot platform as you will be able to access various amazing benefits such as Doubt Clarification Sessions, Cost Effective Prices, Expert Staff Guidance, and a lot more.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are fungi?
Organisms that are omnipresent and consist of a cell wall, are classified as a species under the Kingdom Fungi.
Which fungi group does not produce asexual spores?
Fungi subspecies known as Basidiomycetes, are not capable of producing asexual spores.
What is one example of the kingdom fungi?
A few examples of kingdom fungi can be the eukaryotic organisms comprising microorganisms like yeasts, mushrooms, and molds.
What is the importance of fungi?
There are multiple uses that are mostly an inherent part of fungi structure. These can be:
- Fungi act as a source of food for multiple organisms in the ecosystem.
- Yeast, a form of fungi, is capable of producing Vitamin B. This is used to make various types of baking products like bread.
- Besides, food production, fungi also act as a decomposer.
- In addition to this, fungi also play an active role in the production of antibiotics such as Penicillin.
- Furthermore, fungi are actively used as a pesticide, in order to reduce or eliminate the insects and pests feeding on crops.
