What is Plant Kingdom? Classification, Characteristics, Diagram
The Plant Kingdom, also known as Kingdom Plantae, constitutes many organisms ranging from tiny mosses to towering trees. Understanding the Plant Kingdom is crucial for biologists and nature enthusiasts alike. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the Plant Kingdom, covering its classification, characteristics, and visual representation through the diagram.
Understanding the Kingdom Plantae
The Kingdom of Plantae is a vast and diverse group of organisms that encompass many plant species. From towering trees to delicate flowers, the Plant Kingdom is a testament to the beauty and complexity of nature. Plants are essential for life on Earth, playing a crucial role in oxygen production, food supply, and ecosystem balance.
What is the Plant Kingdom?
The Plant Kingdom, also known as Kingdom Plantae, constitutes many organisms ranging from tiny mosses to towering trees. Understanding the Plant Kingdom is crucial for biologists and nature enthusiasts alike. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the Plant Kingdom, covering its classification, characteristics, and visual representation through diagrams.
Schematic of Plant Kingdom Diagram
Visualizing the structure of the Plant Kingdom is essential to grasp its vast diversity. The schematic of a Plant Kingdom diagram provides a clear representation of the different plant groups and their relationships.
By exploring this diagram, we can gain a deeper understanding of the intricate patterns within the plant world. This visual aid will help you connect the dots as we explore the various branches of plant life. Feel free to refer to the diagram below while reading to enhance your understanding.
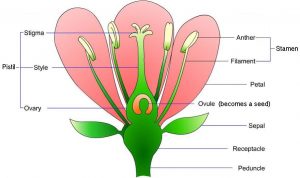
Delving into a Complete Plant Kingdom Classification
The Plant Kingdom is classified into various subgroups based on their distinct characteristics and evolutionary relationships. Let’s explore the different divisions within the Plant Kingdom:
1. Thallophyta
Thallophytes are the simplest of plants, often appearing as multicellular but without true roots, stems, or leaves. Algae is a classic example of Thallophyta. These plants play a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems, contributing to oxygen production and serving as a fundamental part of the food chain.
2. Bryophyta
Mosses and liverworts fall under Bryophyta. Unlike Thallophyta, these plants have primitive structures resembling leaves and stems. They lack vascular tissues, relying on diffusion for nutrient transport. Bryophytes are often found in moist environments and play a significant role in soil stabilization.
3. Pteridophyta
Ferns take the center stage in Pteridophyta. With more developed structures like leaves and vascular tissues, these plants represent a significant leap in complexity. Ferns reproduce through spores, showcasing a unique aspect of their life cycle.
4. Gymnosperms
Gymnosperms, including conifers and cycads, boast seeds not enclosed in a fruit. The development of seeds marked a critical evolutionary milestone. Gymnosperms are hardy plants, well-adapted to diverse environments, and they often dominate cold and arid regions.
5. Angiosperms
Angiosperms, or flowering plants, are the most advanced and diverse group in the Plant Kingdom. Their seeds are enclosed within fruits, contributing to their widespread distribution. From the smallest wildflowers to the tallest trees, angiosperms have conquered nearly every corner of the Earth.
Key Characteristics of Plant Kingdom
The Plant Kingdom exhibits several key characteristics that set it apart from other living organisms. Understanding these traits can provide insights into the unique nature of plants:
Now that we’ve explored the classifications, let’s pinpoint the characteristics that tie all these diverse plants together.
- Autotrophic Nutrition: Plants produce their food through photosynthesis, utilizing sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
- Cell Wall: Plant cells have a rigid cell wall composed of cellulose, providing structural support and protection.
- Multicellular Structure: Most plants are multicellular organisms with specialized tissues for various functions.
- Alternation of Generations: Plants undergo a life cycle alternating between a haploid (gametophyte) and a diploid (sporophyte) phase.
- Adaptability: Plants have evolved diverse adaptations to survive in different environments, from deserts to rainforests.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Plant Kingdom is a testament to the remarkable diversity and complexity of plant life on Earth. By exploring the intricacies of plant classification and characteristics, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the vital role that plants play in sustaining life. Let’s continue to marvel at the wonders of the Plant Kingdom and nurture our connection with the natural world. Start your journey into the fascinating world of plants today!
Keen on mastering subjects effortlessly, just like the example provided? Explore our Tutoroot Blog for simplified learning, where you can enhance your understanding of various topics. Clear up any queries you may have through Tutoroot’s online tuition platform. Take the plunge into the world of Tutoroot’s online home tuitions by scheduling a Complimentary FREE DEMO session today.
Explore the informative biology blogs available on the Tutoroot website to enhance your understanding of key concepts. With Tutoroot’s personalised Biology online tuition, you can tailor your learning experience to suit your individual needs and pace. Whether you’re looking for extra practice or a deeper understanding, Tutoroot offers customised lessons designed just for you. Begin your learning journey with a FREE DEMO session, giving you a firsthand look at how one-on-one online guidance can improve your skills. Experience the advantages of having a dedicated tutor by your side, helping you to master Biology more engagingly and effectively.
FAQs
What are some examples of Kingdom Plantae?
Examples of Kingdom Plantae include roses, sunflowers, ferns, mosses, pine trees, and many more.
What is the Plant Kingdom?
The Plant Kingdom is a major group in the biological classification system that includes all plants. These organisms are primarily characterized by their ability to undergo photosynthesis.
Can you provide some examples of Thallophyta?
Algae is a notable example of Thallophyta, commonly found in aquatic environments and contributing significantly to oxygen production.
