Control and Coordination Class 10 Notes – Complete NCERT Summary
Control and Coordination Class 10 is one of the most important chapters in Science. It helps students understand how the body maintains balance through the nervous and endocrine systems.
These Control and Coordination Class 10 Notes are ideal for CBSE students preparing for board exams, especially when paired with Tutoroot’s CBSE Online Tuition, designed to make Science learning easy, engaging, and result-oriented.
📘 What is Control and Coordination?
Every living being continuously interacts with its environment. To respond effectively to changes (stimuli), the body needs a control and coordination system.
In humans, control and coordination occur through:
-
Nervous System — using electrical impulses
-
Endocrine System — using hormones
In plants, coordination occurs through plant hormones and tropic movements.
🧩 Control and Coordination in Humans
1. The Nervous System
The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
It controls all voluntary and involuntary actions by transmitting electrical impulses.
Key Terms:
-
Neuron: Basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
-
Synapse: Junction between two neurons.
-
Reflex Action: Quick, automatic response to a stimulus (e.g., withdrawing hand from a hot object).
2. Types of Neurons and Nerve Impulse Flow
There are three main types of neurons:
-
Sensory Neuron: Carries information from sense organs to the spinal cord or brain.
-
Relay Neuron (Interneuron): Connects sensory and motor neurons.
-
Motor Neuron: Carries signals from brain/spinal cord to muscles or glands.
Flow of Nerve Impulse:
Stimulus → Receptor → Sensory Neuron → Spinal Cord/Brain → Motor Neuron → Effector (muscle/gland)
3. Reflex Action and Reflex Arc
A reflex action is an involuntary, instant movement in response to a stimulus.
The pathway followed by the nerve impulse during a reflex is called a reflex arc.
Example: Touching a hot object → Impulse travels to spinal cord → Returns to muscles → Hand moves away before you even think.
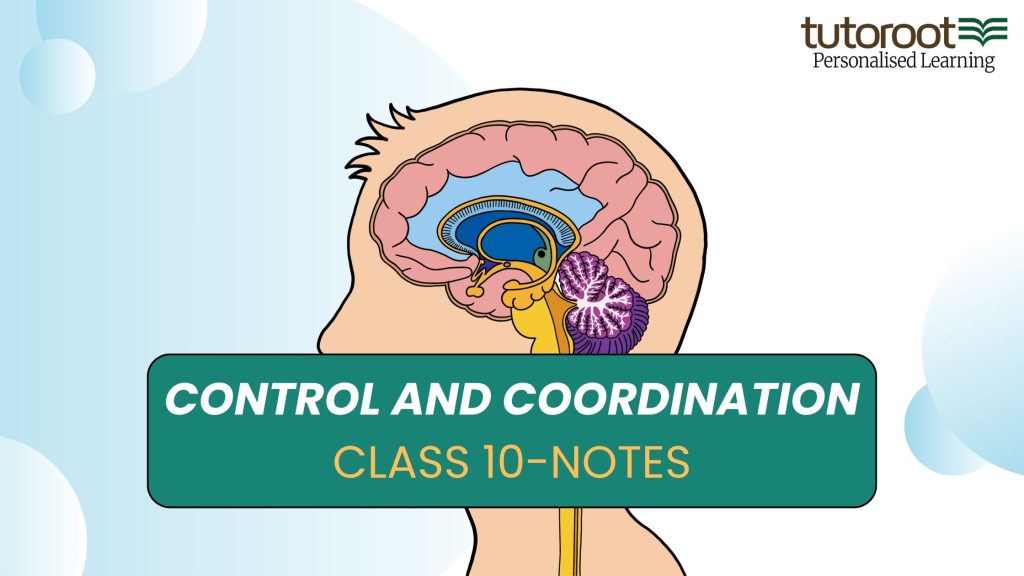
4. Human Brain — Structure and Function
The human brain is the control center of the body and is divided into three main parts:
-
Forebrain: Controls reasoning, memory, and voluntary actions (includes cerebrum).
-
Midbrain: Controls eye and ear reflexes.
-
Hindbrain: Includes cerebellum (balance, posture) and medulla oblongata (heartbeat, breathing).
🌿 Coordination in Plants
Plants do not have a nervous system, but they respond to stimuli using plant hormones and tropic movements.
Plant Hormones
| Hormone | Function |
|---|---|
| Auxins | Promote cell elongation; cause phototropism |
| Gibberellins | Stimulate stem and fruit growth |
| Cytokinins | Help in cell division; delay ageing |
| Abscisic Acid (ABA) | Inhibits growth; helps in stress conditions |
Tropic Movements
| Type | Response To |
|---|---|
| Phototropism | Light |
| Geotropism | Gravity |
| Hydrotropism | Water |
| Thigmotropism | Touch |
Example: Shoots bend toward light → Positive phototropism.
🧬 Hormonal Coordination in Animals
Animals use endocrine glands to release hormones into the bloodstream. These regulate major body functions.
| Hormone | Gland | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Insulin | Pancreas | Regulates blood sugar |
| Adrenaline | Adrenal glands | Prepares body for “fight or flight” |
| Thyroxine | Thyroid | Controls metabolism |
| Growth Hormone | Pituitary | Controls body growth |
| Estrogen/Testosterone | Gonads | Controls reproductive functions |
🔁 Feedback Mechanism in Hormonal Control
The feedback mechanism maintains hormone balance in the body.
Example:
-
Low thyroxine → Pituitary releases TSH → Thyroid secretes more thyroxine.
-
Normal thyroxine → Pituitary reduces TSH.
👉 This self-regulating process is called a feedback mechanism.
⚖️ Difference Between Nervous and Hormonal Control
| Feature | Nervous Control | Hormonal Control |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Electrical | Chemical |
| Speed | Very fast | Slow |
| Duration | Short-term | Long-lasting |
| Pathway | Through neurons | Through bloodstream |
| Example | Reflex action | Insulin regulation |
❓ Important Questions for Board Exams
-
Define reflex action and give an example.
-
Explain the structure of a neuron.
-
Name three types of neurons and their functions.
-
Differentiate between nervous and hormonal control.
-
What is the role of thyroxine in the body?
-
Describe the feedback mechanism of hormone regulation.
-
What are plant hormones? Name any two with functions.
-
Explain the structure and function of the human brain.
-
What is phototropism? Give an example.
-
What is the importance of coordination in organisms?
✨ Summary of Control and Coordination
-
Humans coordinate through the nervous and endocrine systems.
-
The brain controls voluntary and involuntary actions.
-
Reflex arcs provide quick, protective responses.
-
Plants use hormones and tropic movements to respond to stimuli.
-
Hormones regulate growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
-
Feedback mechanisms maintain balance in hormone levels.
🔍 FAQs
Q1. What is Control and Coordination Class 10?
It’s Chapter 7 of the CBSE Class 10 Science syllabus, explaining how organisms control body functions using the nervous and endocrine systems.
Q2. What is a neuron?
A neuron is the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system that carries impulses.
Q3. What are the main topics in Control and Coordination Class 10 Notes?
Neurons, reflex arc, human brain, plant hormones, tropic movements, and hormonal coordination.
Q4. What is the feedback mechanism?
It’s the process by which the body regulates hormone levels — e.g., thyroxine control by TSH.
🎓 Turn Science Struggles into Success Stories with Tutoroot
Struggling with tough chapters like Control and Coordination, Life Processes, or Electricity?
At Tutoroot, we make Science easy to understand and score high with our 1-to-1 Online Tuition Classes.
With expert CBSE tutors, concept-based learning, and interactive visuals, every student gets the clarity and confidence needed to excel in board exams. Our personalised learning plans ensure your child studies smarter — not harder.
📞 Book a Free Demo Class Today and experience how Tutoroot turns complex Science concepts into simple, scoring lessons!
Also Visit Tutoroot Social Platforms –


