Aerobic And Anaerobic Respiration – Definition, Difference
All living organisms, regardless of their shape, size, and type, depend on cellular respiration, as it plays a major role in the breaking down of glucose molecules, and converting them to energy. This is essential for performing various processes in each living organism, and important for their growth and evolution. Besides, based on whether the oxygen is consumed during the process, respiration is differentiated into two types, Anaerobic, and Aerobic respiration.
What is Respiration?
While we step into the broader aspects and difference between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration, we shall first understand what respiration is: Respiration is defined as the process in which the living organism converts all the glucose or food molecules into energy molecules. As mentioned above, respiration is differentiated into two types:
- Aerobic Respiration.
- Anaerobic Respiration.
What is Aerobic Respiration?
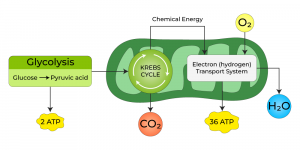
As the title suggests, Aerobic respiration is a typical cellular respiration process that occurs in the presence of oxygen, where energy is produced from food. The aerobic respiration in living organisms like animals, oxygen is most common. Under aerobic respiration, the oxygen is transported to every corner, organ, and cell in the body. This in turn consumes oxygen molecules to convert glucose or food into energy by releasing carbon dioxide. This entire process is called Aerobic Respiration.
What is aerobic respiration in biological terms?
In biological processes, aerobic respiration refers to the conversion of food glucose into energy, in the presence of oxygen. By splitting glucose molecules with oxygen gas aid, energy is released. The byproducts and end products realized at the end of the reaction include energy, water molecules, and carbon dioxide.
In the case of plants, as part of aerobic respiration, oxygen enters plant cells through stomata that are present in the epidermis of leaves and the stem of a plant. Through photosynthesis, plants synthesize food and release energy.
Aerobic respiration is a continuous process taking place inside the plant and animal cells.
Please refer to the aerobic respiration diagram for a clearer understanding of the concept through illustration.
Aerobic Respiration Formula
The above-explained process can be simply explained through the equation,
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
Steps of Aerobic Respiration
There are four stages in the process of aerobic respiration takes place:
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the beginning of aerobic respiration that occurs in the cell’s cytosol. Under glycolysis, the glucose molecules split and segregated into ATP and NADH molecules, numbering two each. Later, these help the process of aerobic respiration.
Formation of Acetyl Coenzyme A
The formation of acetyl coenzyme is referred to as the second stage in aerobic respiration. Under this, pyruvate is oxidized in the mitochondria leading to the production of a 2-carbon acetyl group. This combines with coenzyme A and releases acetyl coenzyme A.
Citric Acid Cycle
A critical step in aerobic respiration, the citric acid cycle is also referred to as the Krebs cycle. This stage of Aerobic respiration is witness to the combining of oxaloacetate and acetyl-coenzyme A, leading to the release of citric acid. There are a chain of reactions undergone by the citric acid cycle, thus producing 2 molecules of carbon dioxide, 1 molecule of ATP, and NADH and FADH, in reduced forms.
Electron Transport Chain
The final stage in aerobic respiration is the electron transport chain, where heavy quantities of ATP molecules are released when electrons from NADH and FADH are transferred. About 34 ATP molecules can be created from one glucose molecule.
What is Anaerobic Respiration?
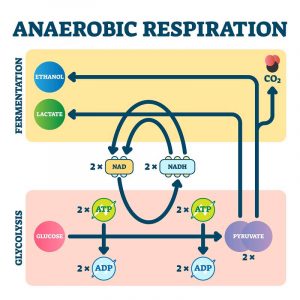
Before we understand the process and the concept of anaerobic respiration, let us first take note of the genesis of the word. The term anaerobic means without air. So, in the obvious sense, anaerobic respiration happens in the absence of oxygen.
Some plants and organisms will not have sufficient oxygen to transport all cells, and in these types of organisms, energy production should not be stopped, as it is essential for them. Thus, for this process, certain multi-cellular organisms perform the breakdown of glucose molecules in each cell and produce carbon dioxide, alcohol, and energy.
Besides, this type of respiration is used by multi-cellular organisms, temporarily in the absence of oxygen. For example, humans, while doing heavy exercises or running, need more energy to continue their workouts, and at that time, their bodies won’t be able to supply enough oxygen to all cells. In this case, the cells are produced through Anaerobic respiration, at the end of which, people generally experience muscle cramps.
Formula of Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic Respiration is explained by the equation,
Glucose → Alcohol + Carbon dioxide + Energy
Glucose → Lactic acid + Energy
Steps of Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration occurs, for example in humans, as a response to oxygen-less conditions. This is generally a temporary phase. Consider intensive exercise and workouts such as cardio (brisk walking, running, sprinting, cycling, or swimming), when heavy energy is sought by the body. The oxygen supply remains limited and this is when muscle cells take to anaerobic respiration to meet their energy needs without the presence of oxygen.
Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
There are multiple differences between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respirations, which we are going to explain briefly here in this section.
| Parameter | Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
| Oxygen | Oxygen plays an important role in the process. | Oxygen is not required for this process. |
| Resulting Components | Carbon Dioxide, Water, and Energy are the resulting components of Aerobic Respiration. | Alcohol, Carbon Dioxide, and Energy are the resultant components of Anaerobic Respiration. |
| Location | Aerobic Respiration is commonly observed in Mitochondria and Cytoplasm. | Anaerobic Respiration is observed in Cytoplasm. |
| Examples | Higher Organisms like Mammals. | Lower Organisms like Bacteria, Yeast, etc. |
Conclusion
Now that you have a good understanding of Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration, its differences, diagrams, and Formulas. If you are struggling with any topics or chapters in this subject, then it would be a good idea for you to join online coaching programs. And currently, the Tutoroot platform is offering a cost-effective Online Home Tutor program for students, with various amazing features. To learn more about these features, go visit the Official website.
FAQ’s
What are the types of respiration?
There are two types of respiration – Aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration, the former being cellular respiration with the presence of the oxygen gas, while the latter is respiration without the presence of the oxygen gas.
Definition of respiration?
Respiration is defined as the process in which the living organism converts all the glucose or food molecules into energy molecules
What is the respiration process?
The respiration process is broken into two stages, inspiration and expiration. Under the chemical process of respiration, food particles are broken down in the cells, with the presence of oxygen, leading to the release of energy.
What is Aerobic Respiration? What are the examples?
Aerobic respiration is a typical cellular respiration process that occurs in the presence of oxygen, where energy is produced from food. The aerobic respiration in living organisms like animals, oxygen is most common. Under aerobic respiration, the oxygen is transported to every corner, organ, and cell in the body. This in turn consumes oxygen molecules to convert glucose or food into energy by releasing carbon dioxide. This entire process is called Aerobic Respiration.
In biological processes, aerobic respiration refers to the conversion of food glucose into energy, in the presence of oxygen. By splitting glucose molecules with oxygen gas aid, energy is released. The byproducts and end products realized at the end of the reaction include energy, water molecules, and carbon dioxide.
What is Anaerobic Respiration? What are the examples?
The term anaerobic means without air. So, in the obvious sense, anaerobic respiration happens in the absence of oxygen.
Some plants and organisms will not have sufficient oxygen to transport all cells, and in these types of organisms, energy production should not be stopped, as it is essential for them. Thus, for this process, certain multi-cellular organisms perform the breakdown of glucose molecules in each cell and produce carbon dioxide, alcohol, and energy.
Besides, this type of respiration is used by multi-cellular organisms, temporarily in the absence of oxygen. For example, humans, while doing heavy exercises or running, need more energy to continue their workouts, and at that time, their bodies won’t be able to supply enough oxygen to all cells. In this case, the cells are produced through Anaerobic respiration, at the end of which, people generally experience muscle cramps.
What are the major differences between Aerobic Respiration and Anaerobic Respiration?
- In aerobic respiration, oxygen is present while in anaerobic respiration, oxygen is absent
- In the case of aerobic respiration, gases are exchanged while this is not the case in anaerobic respiration
- Aerobic respiration is found in the cytoplasm and the mitochondria whereas anaerobic respiration is found only in the cytoplasm.
- In the case of aerobic respiration, glucose breaks down into carbon dioxide and water but in aerobic respiration, glucose breaks down into ethyl alcohol, carbon dioxide, and energy.
- All higher organisms such as mammals have aerobic respiration. Lower organisms such as bacteria and yeast use anaerobic respiration. In other organisms, anaerobic respiration occurs during heavy activities.
