What is Nucleus? – Definition, Structure, Diagram
All living organisms require the nucleus to regulate and actively perform various important functions. However, there are also cells that do not have any nucleus, even though their components and functions are quite familiar to the organisms that have a nucleus. And here in the below article, we are going to discuss Nucleus, its definition, structure, components, and many more in much more detail. Through a nucleus diagram, let us analyze the functions of the nucleus, its structure of the nucleus, and where the nucleus is located, in a more elaborate way,
What is a Nucleus?
Before we analyze the functions of nucleus, along with the structure of nucleus, let us get its fundamental definition. The nucleus is defined as a double-membraned cell organelle, which is a eukaryotic cell, that generally contains genetic material. Although, you must remember that as said above, the prokaryotic cells do not have any nucleus in them. However, there is one cell type that originates from the Eukaryotic cells, but it does not contain a nucleus. These cells are called RBCs. The nucleus happens to be the first discovered organelle.
Structure of Nucleus
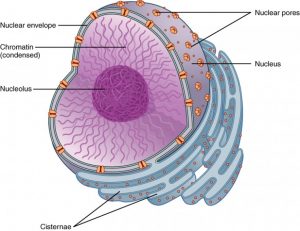
As we step into the deeper understanding of the structure of the nucleus, let us first take note of the fact that the nucleus is an organelle that is spherical shaped. It is present in every eukaryotic cell and is the key component that regulates the functioning of eukaryotic cells. In a eukaryotic cell, there is normally only a nucleus. However, there are eukaryotic cells that are defined as enucleate cells or cells without a nucleus. One of the popular examples is red blood cells. Then there are multinucleate ones with two or more nuclei, such as slime mold.
As far as the structure of the nucleus is concerned, it consists of the nuclear membrane, chromosomes, nucleoplasm, and nucleolus. The most vital organelle it is, the nucleus comprises over 10 percent of the volume of the cell.
The nucleus stays divided from the remaining portion of a cell or the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane.
Nucleoplasm or karyoplasm refers to the matrix located inside the nucleus. As explained earlier, the membrane separates nucleus components from the cytoplasm. The nucleus of the cell contains DNA, which in turn determines the function and shape of the cell, including its growth.
Parts of Nucleus
The Structure of the nucleus in parts:
- Nuclear membrane or envelope or karyotheca
- Chromatin threads or nuclear reticulum
- Nuclear sap or nucleoplasm or karyolymph
- Nucleolus
Nuclear Membrane
A double-layered system that envelopes the nucleus and its constituents. In between the two layers, one can see a space filled with liquid. The large number of nuclear pores let the nucleus get through the rest of the cell or the cytoplasm. The nuclear membrane constitutes lipoproteins, pores, annuli material, perinuclear space, and an inner dense lamella.
Chromosomes
Chromosomes assume the shape and form of DNA strings and protein molecules called chromatin. It is a nucleoprotein that is made up of nucleic acid and basic protein histone.
Nucleic Acids are of Two Types,
- DNA and RNA
- Nucleolus
Assuming the shape of a sphere and seen inside the nucleus, which can have four nucleoli in the case of a few eukaryotic organisms, the nucleolus is crucial for protein synthesis where ribosomes are produced. These ribosomes which are organelles, are made up of RNA and proteins and are transferred to the cytoplasm, where they are blended with endoplasmic reticulum. The ribosome is the protein-producing organelle of a cell. It is the end of the story for the nucleolus whenever a cell is exposed to division and changes after the division.
Functions of Nucleus
Now that you have a good idea about the Nucleus, its structure, and its characteristics. Let us talk about the various functions performed by the Nucleus.
The nucleus is the most crucial and key control point that regulates the gene and gene expressions in any life. It is the repository of genetic material of any organism. This material can be DNA, RNA, or chromosomes.
- It controls hereditary characteristics in any organism
- Responsible for synthesis of protein, growth, and division of cell.
- As per the functions of cell nucleus, various components handle various functions. For example, the nucleolus is meant for protein and RNA storage. In the case of the nucleus, transcription that produces RNA for protein synthesis is a key function.
- The chromatin handles the ribosomes production in the nucleolus and during the cell division, chromatins get themselves arranged into nucleus chromosomes.
- The nucleus functions as the exchange of hereditary molecules that is RNA and DNA between the nucleus and the rest of the cell.
- Energy molecules and regulatory factors are dynamically moved
As per the conclusion of the article, we have learned about the nuclear structure and functions. We have also learned about different types of cells based on the presence and absence of the nucleus.
Conclusion
And in the end, it is safe to say that, in biology, there are multiple chapters or topics, that are very hard to understand or learn. Thus, if the students have any issues with these topics or chapters, then it would be a good idea for them to join online interactive classes. And one such platform which is currently offering cost-effective Online Home Tutor programs for students is Tutoroot. Besides, under this program, the students can access various amazing benefits or features such as exclusive doubt-clearing sessions, access to the best educational guides, expert staff guidance, and a lot more.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does the nucleus do?
As said above, the nucleus performs various important functions, including storing DNA, RNA, and Proteins, as well as growth and metabolism.
Where is the nucleus located?
The nucleus is located in the middle of the Eukaryotic cells, which are commonly found in both animals and plants.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The main nucleus functions are described below,
- It stores the hereditary information of cells or living organisms.
- It plays a major role in controlling reproduction and cell growth.
- It performs DNA replication, which plays an active role in the first stage of cell division.
- Furthermore, the nucleus is the location where the duplicates of DNA and RNA are created, as a result of various cellular processes.
- After this process, the nucleus helps in converting the DNA and proteins into RNA.
- Besides, the nucleus also controls the process of enzyme synthesis.
What is the nucleus?
The nucleus is defined as a double-membraned cell organelle, which is a eukaryotic cell, that generally contains genetic material. Although, you must remember that as said above, the prokaryotic cells do not have any nucleus in them. However, there is one cell type that originates from the Eukaryotic cells, but it does not contain a nucleus. These cells are called RBCs.
