What is Respiration in Plants? – Types, Importance
Introduction
Respiration is a fundamental process that occurs in animals and plants. While plants may seem stationery and passive, they are constantly engaged in complex respiratory activity. In this article, we will unravel the mysteries of respiration in plants, exploring its types, importance, and the intricate processes that take place within different parts of a plant.
What is Respiration in Plants?
Before delving into the specifics, let us first understand what respiration in plants entails. Respiration in plants refers to the biochemical process through which they obtain energy by breaking down organic molecules, such as glucose, and converting them into a usable form known as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This energy is then utilized by plants to perform various vital functions, including growth, reproduction, and defense against pathogens.
Respiration in Plants Equation
The respiration process in plants can be summarized by the following equation:
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy (ATP)
This equation represents the overall chemical reaction that occurs during respiration in plants. Plants take in glucose (a form of sugar) and oxygen from their surrounding environment and release carbon dioxide and water vapor as byproducts. Through this process, plants generate the energy they require to carry out essential metabolic activities.
Respiration in Plants Diagram
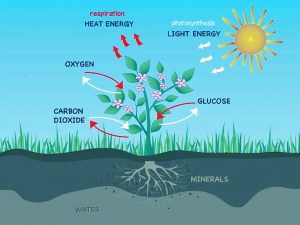
The diagram above provides a visual representation of the respiration process in plants. It illustrates the intake of glucose and oxygen, the production of carbon dioxide and water, and the release of energy in the form of ATP.
Types of Respiration
Respiration in plants can occur through two primary mechanisms: aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration.
Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic respiration is the most common form of respiration in plants. It requires the presence of oxygen and involves the complete breakdown of glucose molecules. Through a series of enzymatic reactions, glucose is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water, releasing a significant amount of energy in the process. This energy is then stored as ATP and utilized by the plant for various physiological processes.
Anaerobic Respiration
Unlike aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen. It is less common in plants but can take place under certain conditions, such as when oxygen availability is limited. During anaerobic respiration, glucose is partially broken down, leading to the formation of byproducts such as ethanol or lactic acid, depending on the specific metabolic pathway involved.
Check Detailed information about Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration here “Aerobic And Anaerobic Respiration – Definition, Difference”
Complete Process of Respiration in Plants
Now that we have a basic understanding of the types of respiration in plants, let us delve into the complete process of respiration in different plant organs.
Respiration in Roots
Roots play a crucial role in respiration, as they are responsible for absorbing oxygen from the soil. In waterlogged or oxygen-deficient soils, roots may resort to anaerobic respiration. During anaerobic respiration, roots release ethylene and alcohol as byproducts, which can have various effects on root growth and development.
Respiration in Stems
Like roots, stems also respire to meet their energy demands. However, stems primarily rely on aerobic respiration, as they are usually exposed to sufficient oxygen in the atmosphere. Energy generated through respiration in stems is utilized for maintaining structural integrity, transporting water and nutrients, and supporting growth.
Respiration in Leaves
Leaves are the powerhouse of respiration in plants. They possess specialized structures called stomata, which enable the exchange of gases with the atmosphere. Oxygen enters the leaves through stomatal pores, while carbon dioxide, a byproduct of respiration, is expelled. The energy produced in leaf respiration is utilized for photosynthesis, growth, and defense mechanisms.
Respiration in Flowers and Fruits
Flowers and fruits also engage in respiration to support their metabolic activities. This process is particularly important during pollination and seed development. The energy produced through flower and fruit respiration contributes to the growth and maturation of these reproductive organs, ensuring successful reproduction for the plant.
Importance of Respiration in Plants
The significance of respiration in plants cannot be overstated. It serves as a lifeline for their survival and plays a vital role in their overall growth and development. Without respiration, plants would be unable to produce the energy necessary for carrying out essential physiological processes. Additionally, respiration enables plants to adapt to changing environmental conditions, respond to stressors, and defend against pathogens.
In summary, respiration in plants is a complex and indispensable process that allows them to thrive in their environment. It influences their growth, reproduction, and ability to adapt. Understanding the intricacies of respiration in plants deepens our appreciation for the remarkable nature of these living organisms and their ability to sustain life.
Final Notes
Respiration in plants is a vast and fascinating topic with many intricacies. This article has provided a comprehensive overview of the process, its types, and its significance in different plant organs. By shedding light on respiration in plants, we hope to inspire a greater appreciation for the extraordinary abilities of plants and their perpetual quest for survival and growth.
Interested in effortlessly mastering complex concepts, as illustrated above? Explore our Tutoroot Blog section for simplified learning. Improve your understanding of subjects and get your questions addressed through Tutoroot’s online tutoring. Uncover the advantages of Tutoroot’s online home tuition by scheduling a FREE DEMO session today.
FAQs
Q: Define respiration in plants.
Respiration in plants refers to the biochemical process through which they obtain energy by breaking down organic molecules, such as glucose, and converting them into ATP. It is essential for their growth, reproduction, and overall survival.
Q: How does respiration occur in plants?
Respiration in plants occurs through the intake of glucose and oxygen, which are converted into carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. This process takes place in various plant organs, including roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits.
Q: What are the products obtained by anaerobic respiration in plants?
Anaerobic respiration in plants can lead to byproducts such as ethanol or lactic acid, depending on the metabolic pathway involved.
Q: How is respiration in plants different from respiration in animals?
While both plants and animals engage in respiration, there are some key differences. Plants primarily perform respiration in their green parts, such as leaves, stems, and flowers, while animals rely on specialized organs, such as lungs. Additionally, plants can undergo anaerobic respiration under specific conditions, whereas animals mainly rely on aerobic respiration.
