Complete Guide for Alternating Current and Direct Current
As we enter into the broader coverage of Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC), let us first understand what current is how it is important as a major subject of Physics, and how it is distinguished into AC and DC. It is obvious that the current is a very important topic in Physics because the current is a crucial element that runs our lives and the entire world. Learning about current and its divisions, Alternating Current and Direct Current is crucial in understanding several related and other topics or chapters. So, in order to move on to other topics or chapters, the students must focus on understanding the above concepts first. In the below sections, you will understand how AC and DC work, and how can one convert alternating current into direct current.
The current flow in a circuit often changes based on the type of application or its uses. Electric current travels in two paths, one as an alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). The flow of current in AC and DC paths primarily symbolizes the definition or nature of these currents. The difference is seen in the direction in which the electrons flow. In direct current or DC, the electrons travel steadily in one direction. However, in AC or alternating current, they repeatedly change directions, moving forward and then backward.
Let us also understand the characteristics of alternating current or AC, and the characteristics of direct current or DC
What is AC or alternating current?
The current inside a circuit, which changes direction` periodically, from forward to backward is known as the alternating current. This type of current is very commonly used in household equipment, such as fridges, pressure cookers, microwaves, and many more. The alternating current or AC, when observed on a graph, forms a Sine Waveform, which represents curved lines, that describe the electric cycles that are measured per second.
The most important feature of the alternating current or AC is its ability to be transported over long distances easily without any issues or loss of current. The AC is measured in Hertz, and the frequency of AC is between 50 to 60 Hz. AC was first tested back in the year 1832, by following the Principles of Michael Faraday, by making use of Dynamo Electric Generator.
What is DC Current or Direct Current?
As you can understand from the above section, the direct current or DC, unlike the Alterntating current or AC does not change direction periodically. So, this means this type of current flows in a single direction steadily. And this is one of the main reasons why it is actively used to charge batteries or supply power to other common electric devices. For example, electric devices like a flat-screen TV, electric Vehicles, etc. Moreover, in the DC current generally, the electrons will transfer from negative to positive terminals. Besides, the electric devices that use AC generally, will use the DC to charge or power their devices. Unlike the AC, the DC is resistive in nature, and it does not have polarity. Apart from this, the frequency of direct current remains zero.
Circuit Diagrams for AC and DC Currents
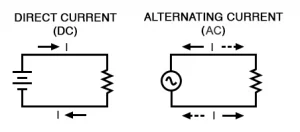
From the above circuit diagrams, you can clearly observe the flow of current in the DC Circuit, as well as the AC Circuit.
Characteristics of Alternating Current or AC
The alternating current or AC displays cyclic positive and negative voltage, featuring the following characteristics, along with advantages and disadvantages of AC
Advantages and Disadvantages of Alternating Current
Advantages of Alternating Current
- The power loss is less because there is high high-voltage transmission
- Shutting down while the power is passing is easier
- Alternating current or AC can be easily transformed through transformers, thus becoming more suited for power supply
- Positive voltage and negative voltage don’t matter at all
Disadvantages of Alternating Current
- Seeks high voltage compared to the target voltage because the voltage value keeps fluctuating, and even touches zero
- Not suited for transmission covering supremely long distances
- Coils and capacitors generate voltage, significantly affecting their flow direction
Characteristics of DC or Direct Current
Advantages of Direct Current or DC
- In the case of direct current, there is no delay or early inside the circuit because the flow direction is constant and so is the voltage
- Direct current stores power, in batteries and capacitors, and so on
- DC does not generate reactive power, ensuring efficiency
Disadvantages of Direct Current or DC
- Current interruption becomes a challenge due to constant voltage, increasing the risks due to power fluctuations
- Showcases strong electrolytic influence
- Voltage conversion is not easy
How to Convert Alternative Current into Direct Current?
The DC Current and AC current are both actively employed in various types of equipment, based on the type of application required, and which is why, they both are employed at the same time, by using equipment such as a transformer to convert alternating current into direct current and vice versa. For this process, a transfer with a power supply needs to be employed, then the direct current is converted into an alternate current using a rectifier.
Moreover, this process is very important to reduce or completely prevent the current from reversing. So that there won’t be any losses while receiving or sending current over long distances. And not just that, the reverse current sometimes causes complete failure or breakdown of equipment.
Difference Between AC and DC
| Parameters | Alternating Current (AC) | Direct Current (DC) |
| Direction | The direction of the current flow changes periodically. | The direction of the current flow does not change. |
| Distance | Safe to transfer current over long distances with little or no loss in power. | Unsafe to transfer current over long distances. |
| Frequency | The Frequency of AC is 50 to 60 Hz. | DC has no frequency. |
| Applications | Electrical Appliances such as Washing Machines, and Refrigerators. | Electrical Appliances such as smartphones, TVs, etc. |
Final Words
We have provided a comprehensive description of the Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current(C) along with circuit diagrams. And we have also listed some of the main differences between AC and DC, and a brief description of the process of converting AC into DC. Students who are facing trouble understanding any topic or chapter in Physics can get the benefits of expert guidance, the best educational guides, doubt-clearing sessions, and many more. Simply joining the Online Interactive Classes offered by the Tutoroot Platform, which will help them understand the topics and chapters easily, and get the best ranks in their examinations
Frequently Asked Questions
What is AC Full Form?
The full form of AC current is Alternating Current, which earned its name due to its change in the direction of current flow periodically.
What is DC full form?
The full form of DC is direct current
What is Direct Current or DC?
the DC Current, unlike the AC Current, does not change direction periodically. So, this means this type of current flows in a single direction steadily. This is one of the main reasons why it is actively used to charge batteries or supply power to other common electric devices. For example, electric devices like a flat-screen TV, electric Vehicles, etc. Moreover, in the DC current generally, the electrons will transfer from negative to positive terminals. Besides, the electric devices that use AC current generally, will use the DC current to charge or power their devices. Unlike the AC Current, the DC Current is resistive in nature, and it does not have polarity. Apart from this, the frequency of DC Current remains zero.
What is Alternating Current or AC?
The current inside a circuit, which changes direction` periodically, from forward to backward is known as the Alternating Current. This type of current is very commonly used in household equipment, such as fridges, pressure cookers, microwaves, and many more. The alternating current or AC, when observed on a graph, forms a Sine Waveform, which represents curved lines, that describe the electric cycles that are measured per second.
The most important feature of the Alternating current or AC is its ability to be transported over long distances easily without any issues or loss of current. The AC is measured in Hertz, and the frequency of AC is between 50 to 60 Hz
Difference Between AC and DC
In alternating current, the direction of the current flow changes periodically whereas in direct current, the current flow does not change.
It is safe to transfer current over long distances with little or no loss in power, in case of AC, while it is unsafe to transfer current over long distances.
The frequency of alternating current or AC is 50 to 60 Hz. Direct current or DC has no frequency.
Electrical appliances such as washing machines, and refrigerators in case of AC; electrical appliances such as smartphones, TVs, etc, in case of DC
