Difference Between Sympathetic And Parasympathetic Nervous System
Introduction
The human body is a marvel of intricate systems and networks that work together to maintain harmony and balance. One such system that operates involuntarily, controlling various vital functions, is the autonomic nervous system.
Furthermore, This system is divided into two branches: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the functions, structures, and dissimilarities between these two crucial components of the autonomic nervous system.
What is the Autonomic Nervous System?
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a part of the peripheral nervous system responsible for regulating involuntary bodily functions, such as heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, and more. Unlike the somatic nervous system, which controls voluntary actions, the ANS functions involuntarily and maintains internal homeostasis without conscious effort.

The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a part of the nervous system that works automatically, without us needing to tell it what to do. It is responsible for managing many vital functions in our body, like breathing, heart rate, body temperature, and digestion. The word “autonomic” itself means “self-governing,” which perfectly describes how this system operates without our conscious control.
How Does the Autonomic Nervous System Work?
Think of the autonomic nervous system as a team of superheroes working together to keep our bodies running smoothly. There are two main parts of the ANS: the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). These two teams have different jobs, but they work together to maintain balance and keep us healthy.
Types of Autonomic Nervous Systems
The autonomic nervous system comprises two major divisions: the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). These two divisions often work in opposition, striking a balance to modulate various bodily functions as per the body’s needs and external circumstances.
Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system is often referred to as the “fight or flight” system. It is activated in response to stressful or threatening situations, preparing the body for quick action. When stimulated, the SNS triggers a series of physiological responses that enable the body to cope with the perceived danger effectively.
Functions of the Sympathetic Nervous System
- Increased Heart Rate: The SNS accelerates heart rate, ensuring an adequate supply of oxygenated blood to the muscles during physical exertion or stress.
- Dilated Pupils: Sympathetic stimulation leads to dilated pupils, enhancing visual sensitivity and peripheral vision in threatening situations.
- Bronchodilation: The SNS relaxes the bronchial smooth muscles, allowing increased airflow to the lungs for improved oxygen intake.
- Inhibition of Digestion: Digestion is temporarily suppressed, as the SNS directs blood flow away from the digestive organs to the muscles and brain for better performance.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
In contrast to the sympathetic nervous system, the parasympathetic nervous system is often called the “rest and digest” system. It comes into play during non-stressful situations, allowing the body to conserve energy and engage in restorative functions.
Functions of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
- Decreased Heart Rate: The PNS slows down heart rate, promoting relaxation and conservation of energy.
- Constricted Pupils: Parasympathetic stimulation causes the pupils to constrict, enhancing near vision and focusing on nearby objects.
- Bronchoconstriction: The PNS constricts the bronchial smooth muscles, reducing airflow and conserving energy during restful states.
- Stimulation of Digestion: Digestion is facilitated as the PNS directs blood flow to the digestive organs, enhancing nutrient absorption and metabolism.
Diagrams for Sympathetic And Parasympathetic Nerves
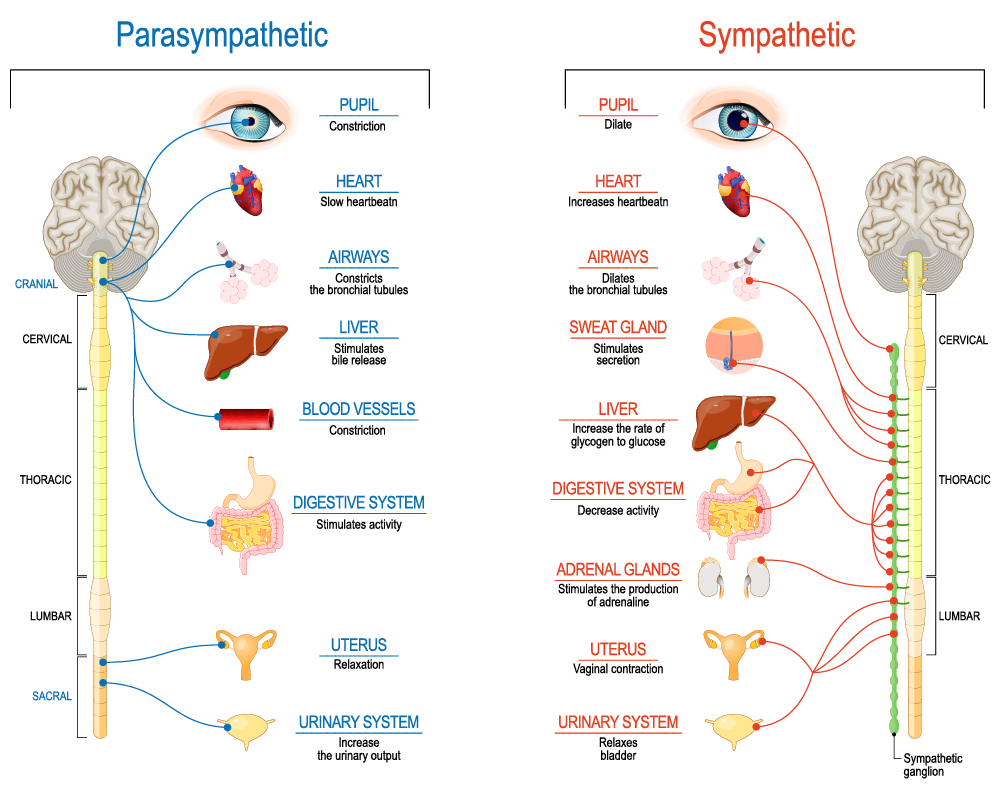
Difference Between the Sympathetic And Parasympathetic Nervous Systems
Now, let’s highlight the key differences between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems:
| Aspect | Sympathetic Nervous System | Parasympathetic Nervous System |
| Activation Response | Fight or Flight – Prepares the body for action | Rest and Digest – Promotes relaxation and recovery |
| Heart Rate | Increases heart rate | Decreases heart rate |
| Pupil Response | Dilates pupils | Constricts pupils |
| Digestive Functions | Decreases digestion | Increases digestion |
| Bronchial Response | Dilates airways | Narrows airways |
| Energy Utilization | Expends energy rapidly | Conserves and restores energy |
| Hormone Release | Triggers release of stress hormones (e.g., adrenaline) | Promotes release of calming hormones (e.g., acetylcholine) |
Final Notes
The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are integral to the autonomic nervous system, ensuring that the body adapts to various situations and maintains internal balance. While the sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for action in response to stress, the parasympathetic nervous system promotes relaxation and restoration during periods of rest.
Understanding the intricate interplay between these two systems sheds light on how the body’s involuntary functions are regulated and orchestrated, helping us appreciate the complexity and efficiency of the human body.
Tutoroot offers the best Online Interactive Classes for various courses like IIT, NEET, and so on. Click here to Book a Free Demo from the expert faculty in the industry, Book Now!
FAQs
Which organ is innervated only by parasympathetic nerves?
The salivary glands are innervated only by parasympathetic nerves. Parasympathetic stimulation triggers the production and release of saliva, aiding in the initial stages of digestion.
When are parasympathetic nerves stimulated?
Parasympathetic nerves are stimulated during restful and non-stressful situations. Activities such as eating, sleeping, and engaging in leisurely tasks promote parasympathetic activation.
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic nervous system is one of the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system. It is responsible for initiating the “fight or flight” response during times of stress or emergency, preparing the body for rapid action.
