What are DNA and RNA? – Difference Between DNA and RNA
DNA and RNA are the fundamental blocks of all life forms on planet earth, which play a major role in carrying genetic information from one generation to another, as well as in the growth and evolution of the species. Thus, it is very important for students to have a good understanding of these topics, as well as their differences. Therefore, to help them out, we have put together a detailed guide about DNA and RNA structure, similarities, and differences here in the below article. Right from the full form of DNA and RNA, to elaborate details, we present a comprehensive picture of these components.
What is DNA?
Let us first learn DNA full form: DNA refers to Deoxyribonucleic acid and is a set of molecules that transport genetic material or information that is vital for an organism to develop and function. DNA is the molecular component that consists of two polynucleotides, that form a complex double helix design that plays an important role in carrying biological and genetic information, and that stores all the instructions for various important processes such as reproduction, growth, functioning, and development of all living organisms. Moreover, each DNA molecule consists of two strands, that store the same biological information of the living organisms.
Each strand is supported by deoxyribose or alternating sugar (referred to as the backbone), and phosphate groups. Four bases are attached to every sugar: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) or thymine (T). Chemical bonds between the bases connect the two strands. These are adenine bonds with thymine, and cytosine bonds with guanine. Along with DNA’s backbone and the bases’ sequence, biological information is encoded.
Friedrich Miescher first founded DNA in 1869, while in 1953, Watson and Crick presented their model that is recognized as the first authentic model of the double-helix of DNA.
Types of DNA
Based on various common factors such as humidity, salt, and ionic concentrations, DNA is differentiated into five types, such as,
- A-DNA – It is said to be the DNA molecule that has the broadest helical diameter among all other forms, and it contains 11 pairs of nucleotides. This type of DNA is commonly found in a region where there is a high concentration of ionic and salt contents.
- B-DNA – One of the most common types of DNA, which consists of neutral PH and physiological concentrations. Moreover, the B-form DNA has 10 base pairs, per turn from the Helix Axis.
- C-DNA – The DNA form, that is commonly observed among the lithium+ ions, and in a region where the humidity is 66% are called the C-DNA molecules.
- D-DNA – The rarest DNA molecule, which has 8 pairs of negatively tilted forms, from the helix ais, is the D-DNA molecule.
- Z-DNA – A DNA form that is commonly found in an environment that has a very high salt concentration is called Z-DNA. One of the most unique features of this DNA is the left-handed helical structure. Moreover, in this DNA, the recurring monomer is a dinucleotide, which makes use of sugar-phosphate linkage to form a zig-zag pattern or backbone.
DNA Structure
The DNA molecules carry instructions that an organism needs to develop, grow, and procreate. Inside each cell, these instructions are stored and passed on from one generation to the other.
As explained above, DNA is composed of nucleotides containing a nitrogenous group, a phosphate group, and a sugar group, the order of the nitrogenous bases being vital in defining and establishing the genetic code {thymine(T), guanine(G), cytosine(C), and adenine(A)}.
The nucleotides are linked together and there are two long strands formed that spiral to create the renowned double-helix. The bases on one strand pair up with the bases of the other. Structure-wise, DNA molecules are very long and are not easy to fit into cells without being properly ordered. The DNA is therefore coiled in a tight manner as to facilitate formations called chromosomes. Each chromosome consists of a single DNA molecule. As far as human beings are concerned, are 23 pairs of chromosomes are stored inside the cell nucleus.
Please refer to the DNA diagram for a clearer and more emphatic understanding
DNA is surely an incredible and most exciting molecule and what we are and how we are is just because of the DNA. When asked ‘what is DNA’, the simple answer in normal parlance is what makes us what we are. Some of the interesting facts are that the DNA of two people can be identical by almost 99.99%. the remaining miniscule, 0.1% is all about differences and variations that clearly establish and define our distinction and uniqueness. These combined with social and environmental and other factors determine our characters and traits, physique and behaviour. A single molecule can make a sea of difference and that is what DNA is all about.
What is RNA?
This nucleic acid, which plays an important role in the process of protein synthesis, is generally referred to as RNA. Its main components are long chains of nucleic acids that are found in all living cells. It acts as a messenger that transfers instructions from DNA, to help in controlling the protein synthesis process. Besides, RNA consists of various components such as nitrogen bases like Adenine (A), Uracil (U), Cytosine (C), and Guanine (G), as well as phosphates and sugar ribose. RNA is primarily a biological macromolecule responsible for protein synthesis and is present in every biological cell.
The major difference between DNA and RNA is that DNA is double-stranded, while RNA is single-stranded. While DNA is the reason for the transmission of genetic information, RNA delivers genetic codes that are vital in the creation of proteins.
The credit for RNA too goes to Friedrich Miescher who discovered Nucleic acids in 1868. He named the material ‘nuclein’ owing to its inherent presence discovered inside the nucleus. However, Leslie Orgel, a chemist who established a world theory of the origin of life, is known as the father of RNA.
RNA Full Form: Ribonucleic acid
Types of RNA
Similar to DNA cells, RNA cells are differentiated into various types –
- TRNA – The Transfer RNA, as its name suggests, plays an important role in the transfer of amino acids to ribosomes.
- RRNA – The ribosomal RNA results in the production of ribosomes with the help of the available proteins.
- MRNA – In Polypeptide, the encoding of amino acid sequences is made with the help of messenger RNA.
- SnRNA – For the processing of RNA in the eukaryotes, the complexes and proteins play an active role, which is generally produced with the help of small nuclear RNA.
Structure of DNA and RNA
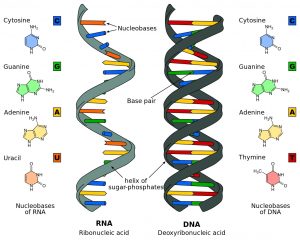
From the above picture, you can understand the various components involved in DNA and RNA structures, along with their chemical compositions, as well as their helix designs.
Difference Between DNA and RNA
DNA and RNA, apart from their similarities, have multiple differences, which we are going to cover briefly here in this section.
| Parameters | DNA | RNA |
| Main Function | It helps in the long-term storage of genetic information. | It involves the transfer of genetic code from the nucleus to ribosomes to make proteins. |
| Type of Sugar Portion | It has 2-deoxyribose. | It consists of ribose. |
| Propagation | DNA replication is automatic. | While RNA cannot replicate on its own. |
| Types of Nitrogenous Bases and Pairing | GC (Guanine pair with Cytosine), AT (Adenine pair with Thymine). | GC (Guanine pair with Cytosine), AU (Adenine pair with Uracil) |
| Location | It is generally located in the mitochondria and nucleus of the cell. | It is found in multiple places, like Nucleus, Cytoplasm, and Ribosome. |
| Full Form | Deoxyribonucleic Acid | Ribonucleic Acid |
| Components | Deoxyribose Sugar, Phosphate Backbone, Thymine, Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine bases. | Ribose Sugar, Phosphate Backbone, Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, and Uracil bases. |
Conclusion
In this article, we have provided a comprehensive description of the structure of DNA and RNA, their differences, and many more. If you find difficulties in any other chapters or topics in this subject, then it would be a good choice to join an online interactive class. And one such online platform, which is offering exclusive and cost-effective Online Home Tutor programs, with various amazing benefits is the Tutoroot platform. If you want to learn more about these features, visit the official platform.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is DNA full form?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
What is RNA full form?
Ribonucleic acid
What is DNA?
DNA is generally defined as a double-stranded molecule, that usually consists of long chains of nucleotides.
What is RNA?
RNA is a single-stranded molecule, which consists of smaller chains of nucleotides.
