What are Analog and Digital Signals? Definition, Difference, Examples

In this article, let us understand the basic and certain advanced concepts of analog and digital signals and their definitions. While we delve deeper into analog signals vs digital signals, we travel an extra mile to read the characteristics of analog and digital signals.
A signal is an electrical or electromagnetic quantity that transports data or information from one system to another. For data transmission, two types of signals are used: Analog signals and digital signals.
Analog and digital signals are very different in many ways. An analog signal is a continuous function, whereas a digital signal is a discontinuous function.
Typically speaking, analog and digital signals are two signal kinds that carry data or information. As far as analog signal vs digital signal is concerned, analog signals feature continuous electrical signals, whereas digital signals are otherwise without continuity in signals.
Types of Signals
Signals are classified into two types:
- Continuous-time signals/ Analog signals: A continuous-time signal is any continuous function of time.
- Discrete-time signals/ Digital Signals: A discrete-time signal is any series of real numbers separated by equal time increments (or samples).
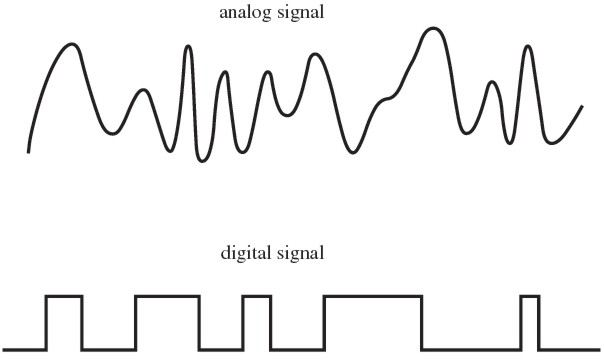
What are analog signals?
Analog signals are used to create information-carrying signals in a variety of systems. Both in terms of quantities and time, these signals are continuous. As the technology evolved, digital transmissions repealed the use of analog signals. Signals that are natural or occur naturally are analog signals. Since it denotes a quantity that is analogous to another measure, it is called so. Analog signals are known for the use of the medium to channel the flow of information. Analog signals can be easily distorted, thereby losing clarity and quality.
Examples of Analog Signal
Any natural sound, human voice, and data read by analog devices are examples of analog signals.
Characteristics of analog signals
Analog signals denote a voltage or any physical quantity that is continuous and invariable and fluctuates in its quantity based on the parameter whose behaviour changes according to time. These can be radio waves, broadcast waves
Further classification of analog signals based on characteristics:
Continuous-time signals and discrete-time signals
Analog signal processing makes use of electronic devices to conduct several operations on the signals. These can range from amplification to limiting. Certain tools used in processing analog signals are analog signal generators, power supplies, oscilloscopes and certain other electronic equipment.
Measuring analog signals
For an analog signal source, its amplitude is measured in volts while the frequency of an analog signal is measured in Hertz. Thus, analog signals carry three categories of information – amplitude, frequency and phase
What is Digital Signal?
A digital signal is a discrete function of time rather than a continuous signal. Digital signals are binary and consist of discrete voltage values at discrete times. A digital signal, in essence, represents data and information as a sequence of discrete values at any given time. The digital signal has a limited number of values.
Characteristics of digital signals
The digital signal is a discrete delivery time and is a non-continuous signal. The bandwidth of digital signals is very high so, they are highly suitable for functions such as computing, digital operations, data storage, etc. The square wave function represents digital signals. These digital signals have fewer fluctuations, healthier instability, and do not fall prey to noise and disturbances, unlike analog signals.
The accuracy and precision of digital signals are also high due to the zero effect of sound on them. They also use less power and give zero errors
Difference between Analog Signals and Digital Signals
The table below highlights all the key differences between Analog and digital transmissions.
| Parameter | Analog Signal | Digital Signal |
| Definition | Analog signals are used to communicate information in a continuous function of time. | A digital signal transmits data in a discrete function of time. |
| Signal values | Analog signals represent data and information using a continuous range of values. | Digital signals use discrete values 0 and 1. |
| Signal bandwidth | The bandwidth is low. | The bandwidth is high. |
| Suitability | Analog signals are better suited for transmitting audio, video, and other data via communication channels. | The digital signals are appropriate for computer and digital electronic processes such as data storage and other things. |
| Effect of electronic noise | Analog signals are easily influenced by electrical noise. | Digital signals are more reliable and resistant to noise than Analog ones. |
| Accuracy | Because analog signals are more susceptible to noise, their accuracy is reduced. | As digital signals are noise-free, they have high accuracy. |
| Power consumption | Analog transmissions require more power to transmit data. | Digital transmissions utilize less power than analog signals. |
| Circuit components | Resistors, capacitors, inductors, and other components | Transistors, logic gates, ICs, etc. |
| Examples | Temperature, current, voltage, voice, pressure, and speed are all examples of analog signals. | Data storage in computer memory is one of the examples of digital signals. |
| Applications | Used in landline phones, thermometers, radios, and other devices. | Used in computers, keyboards, digital watches, and other electronic devices. |
Conclusion
There are many additional challenging topics and chapters in Physics that may be difficult to grasp. Join Physics Online home tuition Programs offered by the Tutoroot platform, it provides several benefits such as low pricing, access to the top educational guides, experienced personnel, doubt-clearing sessions, and many more.
For more simplified explanations like the one above, visit the physics blogs on the Tutoroot website. Elevate your learning with Tutoroot’s personalised Physics online tuition. Begin your journey with a FREE DEMO session and discover the advantages of one-on-one online guidance.
FAQs
What are Examples of Analog Signals?
Current and voltage, pressure, speed, voice and temperature, etc.
What are Examples of Digital Signals?
Digital computers, phones, and data storage are some examples of digital signals
Define Analog Signal
Analog signals are used to create information-carrying signals in a variety of systems. Both in terms of quantities and time, these signals are continuous. As technology evolved, digital transmissions repealed the use of analog signals. Signals that are natural or occur naturally are analog signals. Since it denotes a quantity that is analogous to another measure, it is called so. Analog signals are known for the use of the medium to channel the flow of information. Analog signals can be easily distorted, thereby losing clarity and quality.
Define Digital Signal
A digital signal is a discrete function of time rather than a continuous signal. Digital signals are binary and consist of discrete voltage values at discrete times. A digital signal, in essence, represents data and information as a sequence of discrete values at any given time. The digital signal has a limited number of values.
What are the differences between an analog signal and a digital signal?
Analog signals are used to communicate information in a continuous function of time while a digital signal transmits data in a discrete function of time.
Analog signals represent data and information using a continuous range of values while digital signals use discrete values 0 and 1.
The bandwidth of analog signal is low while it is high for a digital signal.
Analog signals are better suited for transmitting audio, video, and other data via communication channels. The digital signals are appropriate for computer and digital electronic processes such as data storage and other things.
Analog signals are easily influenced by electrical noise. Digital signals are more reliable and resistant to noise than analog ones.
Because analog signals are more susceptible to noise, their accuracy is reduced, whereas, since digital signals are noise-free, they enjoy a higher accuracy.
Analog transmissions require more power to transmit data. Digital signals, on the other hand, utilize less power than analog signals.
