What are Carbohydrates? – Types, Structure, Formula
Introduction and Overview
Carbohydrates can be defined as biological molecules that are formed out of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, in a ratio of approximately a single carbon atom (C) to one water molecule (H2O). The name is derived out of this constitution and is therefore and obviously carbon (carbo-) + water (-hydrate). In a shorter form, carbohydrates are mentioned as carbs.
Carbohydrates are sugar molecules and with proteins and fats, they form the most prominent nutrients in foods and beverages. The metabolism behind their formation is as follows: the body breaks the carbohydrates down into glucose or blood sugar. Glucose is the basic source of energy that keeps us living, i.e., pumping energy into our body cells, organs, tissues, and so on. As we study carbohydrates deeper, we understand that glucose is generally consumed instantly or is stored in the liver and muscles for later use.
Carbohydrates are shown in chains that are measured in various different lengths. In terms of biologically prominent carbohydrates, there are three categories: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Let us delve deeper into various aspects of carbohydrates. Also, we try to explain and understand the classification and structure of carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates definition
A carbohydrate can be defined as a molecule kind that is made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Carbohydrates are sugars or monosaccharides, such as glucose, or are composed of several sugar units or polysaccharides such as glycogen. Carbohydrates play a major role as a source of energy for lives. In simplest terms, carbohydrates are basically a group of organic compounds that are present in foods and living tissues, and in the form of either sugars, cellulose, or starch.
In chemical aspects, carbohydrates are called “optically active polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or the compounds that produce units of such type on hydrolysis”.
Of course, as we explore the classification of carbohydrates or the structure of carbohydrates, the most important point to note is carbohydrates are commonly seen by people as “sugar”, the sucrose disaccharide, extracted from sugar cane or sugar beets, and is sweet.
Classification of carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are classified into monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Based on the structure and hydrolysis-related characters, this classification of carbohydrates is been arrived at.
They are mainly classified into three groups:
- Monosaccharides
- Disaccharides
- Polysaccharides
These complex carbohydrates are generally those single units or monosaccharides that are bonded together. In the case of oligosaccharides, they possess two to ten simple sugar units, whereas polysaccharides contain hundreds and thousands of interrelated monosaccharides. Complex carbohydrates are known for long-lasting energy.
Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides (mono- = “one”; sacchar- = “sugar”) are classified as the simplest sugars of which the most known and common on is glucose. These monosaccharide carbohydrates are that category of carbohydrates for which further hydrolyzing is not possible, where they give much smaller units of polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone. A monosaccharide with an aldehyde group is called aldose, while a monosaccharide carbohydrate with a keto group is called ketose.
The most important monosaccharide carbohydrate is glucose which is prepared out of sucrose or starch.
Monosaccharide carbohydrates’ formula is (CH2O)n, and they typically possess three to seven carbon atoms. Most oxygen atoms in monosaccharides are present in hydroxy (OH) groups, while one of them belongs to carbonyl (CO). In fact, the carbonyl’s position determines the category of sugars. The sugar names also depend on the carbon numbers, trioses have three carbons, pentoses have five carbons, and hexoses are composed of six carbons.
Disaccharides
Disaccharide carbohydrates(di- = “two”) are constituted of two monosaccharides that combine through a dehydration reaction. This is also called a condensation reaction or dehydration synthesis. As part of the process, one monosaccharide carbohydrate’s hydroxyl group joins the hydrogen of another monosaccharide carbohydrate. This results in the release of one molecule of water and eventually the formation of a covalent bond which is called a glycosidic linkage.
In summary, the two monosaccharide units are combined by the oxide linkage that happens due to the loss of water molecules. One of the most common disaccharide carbohydrates is sucrose, which post hydrolysis leads to the formation of glucose and fructose. Also, there are milk sugars, maltose, and lactose, which are well-known types of disaccharides.
Polysaccharide
The third category of carbohydrates – polysaccharides are known for holding long monosaccharide units that are combined again by a glycosidic linkage. A majority of polysaccharide carbohydrates are known to be the points of food storage, like starch which is the principal storage polysaccharide carbohydrate in plants.
A polysaccharide is a polymer of α glucose and has two components- Amylose and Amylopectin. One of the most known polysaccharide carbohydrates is cellulose, a common finding in plants.
About storage polysaccharides
Starch represents the sugar that is in its stored form, in plants, it is composed of two polysaccharides, amylose, and amylopectin (both are polymers of glucose). For plants to be able to synthesize glucose, they make use of the light energy that is collected in photosynthesis. The quantity of glucose in excess of the plant’s energy requirement for the given moment is preserved in the form of starch. This is stored in different parts of the plant parts.
Simple carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are usually categorized under simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates are seen as basic kinds, such as those found in sweets, desserts, sweet snacks, biscuits, and sweet beverages. Typically, simple carbohydrates are those found in foods with processed sugar.
We also find simple carbohydrates in natural sugars that are present in fruits and vegetables, milk, honey, and so on. These natural sugars are eaten in their original form and simple carbohydrates are not complex, as the term suggests. Our bodies easily break them down.
Complex carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates are those that form the most source of energy in our body. Complex carbohydrates ensure energy or fuel is provided in a sustained fashion, as the body needs for daily activities and burnout.
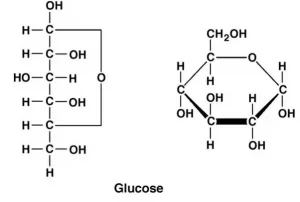
Glucose, the simple sugar, is the most known group of carbohydrates. Its chemical formula is C6H12O6 and is made of six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group. Thus, it is referred to as aldohexose. Glucose is present in two forms, open-chain or acyclic form or ring or cyclic form.
Structure of Fructose
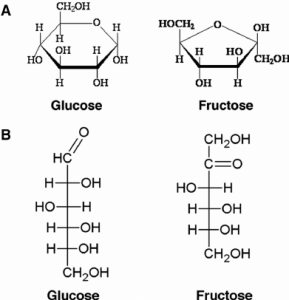
Fructose is classified as a monosaccharide carbohydrate and is also a simple sugar with a chemical formula C6H12O6. Most commonly known as fruit sugar, the crystalline fructose occurs as a cyclic six-membered structure that is delinquent to the stability of the hemiketal and internal hydrogen bonding. This form is referred to as D-fructopyranose. Fructose mainly is seen in root veggies, flowers, honey and vine fruits, while it is commercially processed from maize, sugarcane and sugar beets. Fructose was discovered in 1847 by French chemist Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut.
Carbohydrates Structure
Carbohydrates are substances with the formula Cn(H2O)m. The most common sugars such as glucose and fructose or sucrose have this formula applied to them. Presently, carbohydrates are seen as polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketone with the formula that denotes a molecule closely being related to it, or oligomers or polymers of these molecules.
Monosaccharide is a carbohydrate category derived out of possessing a single carbon chain, whereas disaccharide and trisaccharide carbohydrates refer to molecules that contain two or three such monosaccharide units combined together by acetal or ketal linkages. Then there are Oligosaccharide and polysaccharide carbohydrates that represent larger specifications and dimensions, with a few or more monosaccharide units, respectively.
Carbohydrates formula
Carbohydrates constitute carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O), and the hydrate of carbon is called carbohydrates and it is composed of hydrogen and oxygen in the same proportion as in water.
The general formula of carbohydrates is \(C_{x} ( H_{2}O)_{y}\)
Certain carbohydrates may not align with Cx(H2O)y, formula, such as 2-deoxyribose \(C_{5}H_{10}O_{4}\)
Important Function of Carbohydrates
The most important functions of carbohydrates are:
- Energy production and storage
- Building of macromolecules,
- sparing protein, and
- helping in lipid metabolism
Major Sources of carbohydrates
The following are a few sources of carbohydrates,
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Potato
- Starch
- Grains
- Lentils
- Milk
- Honey
- Corn
- Quinoa
- White bread
Final Notes
Hence, this is all about carbohydrates and their types. In this article, we elaborated on the carbohydrate formula and structure. If you want to learn more concepts visit our blog section.
To understand complex concepts and to overcome the competition in your academics online tuition will play a crucial role. Our personalized online tuition will help in understand complex concepts in a simple way, book an exclusive FREE DEMO now to experience our teaching methodology.
FAQs
Define carbohydrates
A carbohydrate can be defined as a molecule kind that is made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Carbohydrates are sugars or monosaccharides, such as glucose, or are composed of several sugar units or polysaccharides such as glycogen. Carbohydrates play a major role as a source of energy for lives. In simplest terms, carbohydrates are basically a group of organic compounds that are present in foods and living tissues, and in the form of either sugars, cellulose, or starch.
What are the types of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are classified into monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides
What is the general formula of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates constitute carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) and have the general Cx(H2O)y formula.
What are complex carbohydrates?
Complex carbohydrates are those that form the most source of energy in our body. Complex carbohydrates ensure energy or fuel is provided in a sustained fashion, as the body needs for daily activities and burnout.