What are Lipids? – Structure, Function, Types
If you are talking about living organisms of all shapes and forms, in various ecosystems or environments across the world, then it would be essential for you to understand what Lipids are, and why they are very important for the structure and functioning of living organisms. Therefore, to help you out, we have put together a detailed guide about Lipids, the classification of lipids, the characteristics of lipids, and many more.
What are Lipids?
Lipids are generally defined as organic compounds that are generally made up of oxygen, hydrogen, and carbon atoms, which together play an essential role in the formation of the framework of a living cell, and thus for its functioning as well. More importantly, one of the most popular characteristics of Lipids is soluble only in non-polar solvents unlike water, etc. Besides, these organic compounds are commonly found in red meats, milk, cheese, fried food, etc.
Structure of Lipid
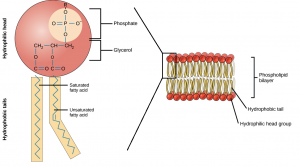
In the above picture, you can observe the various components of lipids, as well as their compositions.
Types of Lipids
Generally, lipids are differentiated into multiple types, mainly, apart from the categorization into two types, Saponifiable and Non-Saponifiable. Types of Lipids such as, Complex Lipids, Simple Lipids, Precursor & Deprived Lipids, Fatty Acids, etc.
Simple Lipids
The esters of fatty acids which consists of various type of alcohols are defined as Simple Lipids. Fats and Waxes are the two popular examples of Simple Lipids.
Complex Lipids
Unlike simple lipids, these esters of fatty acids contain groups involving alcohols and fatty acids. Glycolipids, Phospholipids, Amino Lipids, Sulpho Lipids, and Lipoproteins are some popular examples of Complex Lipids.
Fatty Lipids
Fatty acids as stated above, are also a form of Lipids, which include wider varieties such as long aliphatic tails and carboxylic acids. Besides, Fatty Lipids are differentiated into two types, one is saturated fatty acids, as they do not contain carbon-carbon double bonds, while unsaturated lipids have more than one double bond.
Properties of Lipids
Now that we have a good understanding of the types of Lipids, the Structure of Lipids, etc. Let us now talk about the Properties of Lipids, which we are going to explain briefly here in the below section.
- Lipids are energy-rich organic molecules, that are insoluble in water. However, there are soluble in other organic solvents such as benzene, alcohol, chloroform, and acetone.
- Besides, Lipids generally do not consist of any type of ionic charges.
- Generally, Lipids like Oils, Fats, etc are odorless, tasteless, and colorless.
- These lipids can become non-crystalline solids or liquids when placed at room temperature.
Conclusion
The article above has provided a comprehensive description of lipids classification, types, and characteristics of lipids. If you have doubts about any other topics or chapters in the biology subject. Then it would be a good idea for you to join the Online Interactive Classes offered by the Tutoroot platform. Mainly because, through these classes, you can access various benefits such as Doubt Clarification Seals, Expert Staff Guidance, and many more.
FAQ’s
What is the solubility of lipids in water?
As stated above, lipids are generally insoluble in water.
Where do the lipids and proteins get synthesized?
The endoplasmic reticulum is the region in the cell, where the proteins and lipids get synthesized.
