What is an Ecosystem? – Structure, Definition
An Ecosystem is defined as the functioning of non-living components in conjunction with various types of life forms, which interact with each other. In other words, it can also be described as an interaction between the biotic and abiotic components with said space, for various different purposes. Besides, this, the ecosystems can be differentiated into various types and it includes multiple components, which we will explain briefly here in the below article.
Importance of Ecosystem
Before delving into the concept of a system, it is important to understand the different functions of the ecosystem, such as,

- The ecosystem helps in the maintenance of the flow of energy, including various cycles like the Nitrogen Cycle, Oxygen Cycle, Carbon Cycle, Energy Cycle, and Water Cycle.
- Moreover, it promotes various types of food chains for different living animals existing in the same ecosystem.
- The ecosystem also builds habitats for the survivability of various plants and animals.
- More importantly, the ecosystem is essential for the process of recycling nutrients between abiotic and biotic components, to promote growth.
- Furthermore, the ecosystem manages or controls the various ecological processes that play a very important role in the said ecosystem.
Types of Ecosystems
Now that you have a basic understanding of the Ecosystem, and its significance. Let us talk about the different types of ecosystems, as well as their functions. As you can guess, all ecosystems are primarily differentiated into two types.
Terrestrial Eco Systems
All Land-Based ecosystems are described as Terrestrial Ecosystems, which are differentiated based on the types of geological zones. Types of Terrestrial Ecosystems are,
- Grassland Ecosystem
- Forest Ecosystem
- Desert Ecosystem
- Tundra Ecosystem
Grassland Ecosystem
As the name itself suggests, these types of ecosystems are generally dominated by various types of grasses and herbs. Besides, there are many different grassland ecosystems on our planet like Savannah Grasslands, Tropical Grasslands, and Temperate Grasslands to name a few.
Forest Ecosystem
One of the most essential ecosystems involves animals, microorganisms, plants, trees, etc, that co-exist with the various abiotic factors present in the environment. Mainly because this ecosystem plays a major role in managing the temperature and the ability to absorb the carbon-di-oxide available in the atmosphere.
Desert Ecosystem
The regions or ecosystems with a limited amount of vegetation and rainfall, and are generally dominated by coarse-textured soils. In this type of ecosystem, the days are very hot, while the nights are cold, making it very difficult for the plants and animals to survive.
Tundra Ecosystems
These ecosystems are mostly found in cold arctic or mountain tops, that do not have an adequate amount of rainfall, and the number of trees is generally scarce. More importantly, Tundra Ecosystems are covered with snow most of the time.
Aquatic Ecosystems
The ecosystems which exist in the body of water are called Aquatic ecosystems, and are divided into,
- Marine Ecosystem
- Fresh Water Ecosystem
Marine Ecosystem
The ecosystems which include oceans and seas are generally called Marine Ecosystem, and they generally consist of greater biodiversity compared to other types of ecosystems.
Fresh Water Ecosystem
An aquatic ecosystem that includes various types of biomes, such as wetlands, lakes, rivers, streams, ponds, etc. Besides, this type of ecosystem consists of various unique aquatic life and biodiversity.
Structure of Ecosystem
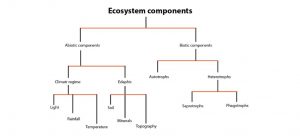
In order to understand the flow of energy in an ecosystem, it is essential to understand the structure of the ecosystem. Moreover, the structure of an ecosystem mainly consists of two components, such as,
- Biotic Components
- Abiotic Components
Biotic Components
Biotic Components involve all types of living beings that are categorized based on the type of nutrition, such as Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers.
- Producers – All plants are called autotrophs, as they have the ability to produce food through the process of photosynthesis. This is why these plants are called producers, as the higher organism depends on these plants for food.
- Consumers – All the organisms which depend on the producers for food are defined as consumers. And these consumers are further differentiated into multiple types like Primary Consumers, Secondary Consumers, Tertiary Consumers, and Quaternary Consumers.
- Decomposers – Saprophytes usually are found in dead and decaying organic matter, and their main purpose is to recycle the nutrients from this matter, to make them sustainable for plants. Fungi and Bacteria are some examples of decomposers.
Conclusion
The above article covered in detail all about the structure and function of the ecosystem, and the type of ecosystem. And if you have any struggles understanding other topics or complex chapters in this subject, then online coaching might be a very good option. Currently, the Tutoroot platform is offering cost-effective online interactive classes for interested students, and through this program, they are providing various unique features such as Expert Staff Guidance, Doubt Clearing Sessions, Access to Best Educational Materials, and a lot more.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of decomposers in the ecosystem?
The primary role of decomposers like fungi and bacteria in the ecosystem is, to break apart the dead inorganic materials, and make these materials consumable for the plants in the surroundings.
Which is not a natural ecosystem?
Generally, Aquariums are not considered a natural ecosystem as they are created artificially by people.
What is ozone and how does it affect any ecosystem?
Ozone is defined as a gas that exists in the upper atmosphere, made out of three oxygen atoms. The main function of the ozone layer is to protect the environment from harmful UV Radiation emitted by the Sun.
