What is Light Emitting Diode (LED) – Working of LED
LEDs or light emitting diodes have been one of the most sought equipment these days, as they are increasingly employed in different applications, such as TVs, smartphones, and many more. Moreover, with the increase in the application of LEDs in every electronic device, different types of light-emitting diodes are invented every day, each using different types of principles. And to help students understand how LEDs work, what are the different types of LEDs available, and their applications. We have put together a detailed guide for you in the article below.
What is an LED?
A Semiconductor device, that emits light when current flows through it, is referred to as LED (LED full form is Light Emitting Diode). However, one thing they must keep in mind, is that the current flow in the LEDs is only on the forward side because the backward flow of current is blocked in this type of semi-conductor.
Moreover, the LEDs or light-emitting diodes consist of heavily doped p-junction diodes. And using these diodes, and the type of semiconductor materials different types of colors are obtained from these LED lights.
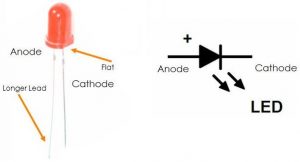
LED Symbol
The symbol for LED or light emitting diode is the standard one of that of a diode where you see an extra two small arrows that symbolize light emission
The LED symbol closely resembles the p-n junction diode. We see anode on the left, and the cathode on the right. What makes them different from each other is that the two arrows denote that the diode is emitting the light.
If we look at the LED circuit, a simple one, we see that it consists of a voltage supply and a resistor that is present to control and regulate the power supply and voltage.
The LED symbol diagram is as shown in figure below,
Circuit Diagram of LED
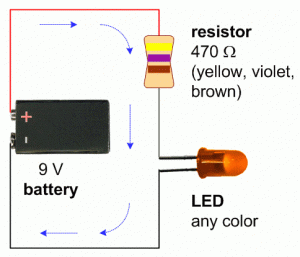
The above picture details the various components involved in an LED Circuit.
The above LED circuit diagram details the various components involved in an LED Circuit. Any LED circuit diagram examples the functioning where, if the diode is forward biased, the minority electrons are sent from p → n while the minority holes are sent from n → p. A close look at the junction boundary, in any LED diagram, one can understand that the concentration of minority carriers increases. The minority carriers in more numbers, found at the junction go on to regroup again with the majority carriers.
Types of Light emitting diodes
Now that we have understood the basics of the LEDs, their circuit, and their symbol. Let us now talk about the different types of LEDs currently available.
High-Power LEDs
As you can guess, from the name itself, these types of LEDs will require high voltage, as they have high luminous intensity and wavelength. However, because of the high intensity of these LEDs, there is a chance of high heating, which in turn will cause the LED to break or diffuse.
Lightning LED
These types have aluminum or ceramic bodies, which help the LED to operate under high voltage and provide more luminosity, by improving heat dissipation.
Miniature LEDs
One of the most popular LEDs, which are actively used in various types of equipment, mostly because of their features such as more luminosity, no need for heat dissipation, etc. Besides, based on the type of application, the miniature LEDs are divided into multiple types such as ultra-high output, standard, and low current.
Flash LED
The Flash LED is a normal LED apparatus, that involves an integrated circuit, which can emit light at a particular frequency. Moreover, unlike the other LEDs, these do not require any type of resistors in them.
Red Green Blue LEDs
These LEDs have three primary colors Red, Green, and Blue, and using these colors they produce a new type of color. Moreover, these LEDs are mainly used in status indicators, light shows, and accent lightning.
Bi and Tri-Color LEDs
Based on the number of light-emitting dies involved in a single case, whether it is two or three, which are used to produce a new color, these LEDs are differentiated into Bi and Tri-Color LEDs respectively.
Alphanumeric LEDs
Alphanumeric LEDs are popularly known for their ability to consume less power while offering greater flexibility. Besides, the result in these types of LEDs is displayed in the form of alphabets or letters and is actively used in watches and calculators.
Working and Functionality of LED
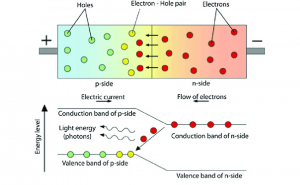
First of all, the LED works on a principle called, Electroluminescence, which involves a material emitting light, as a result, when a current is passed through it. Moreover, as you can see from the diagram when a current passes through the semiconductor, then the electrons attain energy, which in turn will release photons that emit light. Besides, with the increase in the voltage, the intensity of the light emitted by the LEDs increases.
As per any LED circuit diagram, we understand that the energy is always released as photons on recombination. Let us take the case of standard diodes where the energy is released in the form of heat. If we consider light-emitting diodes, this energy assumes the shape and form of photons, and this phenomenon is termed as electroluminescence. In physics, Electroluminescence is referred to as an optical phenomenon. It is also seen as the electrical phenomenon when light comes out of any material because of the passage of current through it. When the forward voltage goes up, the light has its intensity spike significantly, hitting a maximum.
Let us now look at how the hues and colors of light-emitting diodes is determined. This is a result of the material that is used in the semiconducting element. Two primary materials are deployed in LEDs, aluminum gallium indium phosphide alloys and indium gallium nitride alloys. With aluminum alloys, you get red, orange, and yellow light, and through the application of indium alloys, we get to see green, blue, and white light.
Advantages and Disadvantages of LEDs
Pros of LEDs
- LEDs being the latest and technologically advanced, are small and occupy less space
- They consume very little power or voltage compared to incandescent bulbs and are thus more energy efficient.
- LEDs are primarily are flexible in direction and can be turned in any direction without wasting light
- Nothing beats LEDs in being eco-friendly with zero mercury or other hazardous substances
- Generally, LEDs emit monochromatic light, which is not harmful to our eyes.
- The durability and ruggedness of LEDs are far greater compared to normal bulbs. They ensure longer life. they are also known as solid-state lightning since they are made of solid material and have no filament or bulbs or tubes to break or get damaged.
- Moreover, these light-emitting diodes do not require any warm-up time as they light themselves up in nanoseconds
- LEDs (Light emitting diodes) are not affected by temperatures and can even stay strong in subzero temperatures
- Directional – With LED’s you can direct the light where you want it, thus no light is wasted
- LED’s guarantee incredible colour rendering unlike other light sources such as fluorescents
- LEDs are easy to control for brightness and color
Cons of LEDs
- LEDs are generally more expensive than incandescent bulbs.
- When LEDs are exposed to UV or sunlight for a long time, then the color of these bulbs must change.
- Overheating is a possible phenomenon with LEDs.
- Blue issues: it is observed that blue LEDs go beyond the safe limits of the so-called blue-light hazard that has been defined in eye safety specifications. They emit more blue light compared to other light sources, thus causing more light pollution.
- Dependence on ambient temperatures and voltage sensitivity are other disadvantages of LEDs
Properties of LEDs
LEDs have multiple properties which make them unique and more useful, such as,
- This light is highly directional.
- Because waves of light are in a phase of space and time, they are generally coherent.
- Moreover, the laser light emitted by LEDs has only a single color, unlike incandescent bulbs.
Conclusion
The above article provided a comprehensive description of the Working principle of LED, light emitting diode circuits, advantages of LED, and many more. And as you know, Physics contains multiple complex topics and chapters that are hard to understand. So, if you have any troubles in this subject, it would be in your best interest to join an online coaching platform. If you are looking at cost-effective online interactive classes, then Tutoroot might be a good option for you, as it offers various unique features and benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the full form of a LED?
Light Emitting Diode is the full form of LED.
What is LED Principle?
As stated in the above section, the principle of LED is Electroluminescence.
