What are Light reaction And Dark reaction? – Definition, Difference
Introduction to Light Reaction and Dark Reaction
Photosynthesis is a remarkable process that allows plants to convert sunlight into energy, enabling them to grow and produce oxygen as a byproduct. But did you know that photosynthesis consists of two distinct stages known as light reaction and dark reaction? In this article, we will explore the definitions, functions, characteristics, and differences between these two vital components of photosynthesis. Whether you’re a curious eighth-grader or simply want to refresh your knowledge, we’ve got you covered!
What is Light Reaction?
The definition of Light reaction is,
The light reaction, also known as the light-dependent reaction, is the first stage of photosynthesis. It takes place in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts within the plant cells.
Light Reaction Diagram
To provide a visual representation of the light reaction, imagine a complex network of thylakoid membranes arranged in a stacked formation called grana. Within these membranes, there are chlorophyll molecules, as well as various other components such as electron carriers and enzymes.
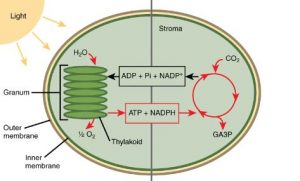
Functions of Light Reaction
The Functions of Light Reaction are,
- Absorption of Light
- Water Splitting
- ATP and NADPH Formation
The functions of light reaction in detailed in further lines,
The primary function of the light reaction is to convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). Both ATP and NADPH are vital energy carriers that play a crucial role in the subsequent dark reaction.
During the light reaction, chlorophyll molecules absorb light energy, exciting their electrons. These energized electrons are passed along a series of electron carriers embedded within the thylakoid membranes. This electron transport chain generates ATP through a process called photophosphorylation.
Furthermore, the excited electrons from chlorophyll are used to reduce NADP+ to NADPH, which will later provide the necessary reducing power for the dark reaction.
Characteristics of Light Reaction
The light reaction exhibits several distinctive characteristics that distinguish it from other metabolic processes:
- It occurs only in the presence of light, as it relies on the absorption of photons by chlorophyll.
- The absorbed light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
- Thus, the rate of the light reaction is directly dependent on the intensity of light available.
- It takes place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts.
- These membranes provide an organized structure for the components involved in the light reaction, maximizing the efficiency of energy conversion.
- It involves both non-cyclic and cyclic electron transport.
- Non-cyclic electron transport generates ATP and NADPH, while cyclic electron transport produces additional ATP.
What is Dark Reaction?
It is the second stage of photosynthesis, the definition of dark reaction is,
The dark reaction or the light-independent reaction, takes place in the stroma of the chloroplasts. Unlike the light reaction, the dark reaction does not rely directly on light. Instead, it uses the chemical energy stored in ATP and NADPH, produced during the light reaction.
Dark Reaction Diagram
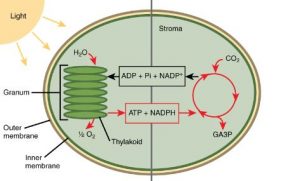
To visualize the dark reaction, picture the stroma, which is the fluid-filled space within the chloroplasts. Within the stroma, there are enzymes and other molecules responsible for carrying out the dark reaction, including the enzyme Rubisco (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase).
Functions of Dark Reaction
The Main functions of Dark reaction are,
- Carbon Fixation
- Glucose Formation
- Regeneration of RuBP
Let’s discuss the functions of Dark reaction in detail,
The dark reaction, also called the Calvin cycle, uses ATP and NADPH produced during the light reaction to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) into glucose, a simple sugar. This process is known as carbon fixation. Rubisco, the enzyme mentioned earlier, plays a critical role in catalyzing the fixation of carbon dioxide.
The ATP and NADPH generated in the light reaction provide the necessary energy and reducing power to drive the complex set of chemical reactions involved in the dark reaction. Ultimately, the dark reaction produces glucose, which serves as a source of energy and building material for plants.
Characteristics of Dark Reaction
The dark reaction possesses several key features that differentiate it from the light reaction:
- It does not directly require light energy.
- However, the chemical energy stored in ATP and NADPH, generated during the light reaction, is essential for the dark reaction to proceed.
- It takes place in the stroma of chloroplasts.
- The stroma provides an aqueous environment and acts as a site for the chemical reactions of the dark reaction.
- It involves a cycle of chemical reactions called the Calvin cycle.
- This cycle includes several intermediate compounds, such as ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, and ribulose-5-phosphate.
- These compounds undergo a series of chemical transformations to produce glucose.
Difference Between Light Reaction and Dark Reaction
The main differences between the light reaction and the dark reaction can be summarized as follows:
Certainly! Here’s a tabular comparison between Light Reaction and Dark Reaction:
| Aspect | Light Reaction | Dark Reaction |
| Location | Thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts | Stroma of chloroplasts |
| Dependency on Light | Requires direct light input | Does not require direct light input, but depends on products of light reactions |
| Products | Oxygen gas (O2), ATP, NADPH | Glucose and other carbohydrates |
| Purpose | Capture and convert light energy into chemical energy | Use chemical energy to fix carbon dioxide and create glucose |
| Time of Occurrence | Occurs during the daytime when sunlight is available | Can occur during the day or night |
| Rate of Occurrence | Faster compared to dark reaction | Slower and can continue even in the absence of light |
This table provides a concise overview of the main differences between light reactions and dark reactions in photosynthesis.
Final Notes
The light reaction and the dark reaction are two interconnected processes that contribute to the overall process of photosynthesis. While the light reaction converts light energy into chemical energy, the dark reaction uses this energy to fix carbon dioxide and produce glucose.
Understanding the intricacies and differences between these reactions provides valuable insight into the fascinating ways in which plants harness and utilize energy from the sun. So, next time you witness the wondrous greenery around you, take a moment to appreciate the remarkable processes occurring within every leaf.
This is the in-depth information of light reaction and dark reaction, Hope this article clears all information about the function of light reaction and dark reaction along with the characteristics of light reaction and dark reaction. Tutoroot offers one-on-one tuition for all the classes to various boards and exams. If you want to experience our interactive online classes, you can book a FREE DEMO now by just clicking here.
FAQ
Where do light reactions occur?
Light reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, which are organelles found within plant cells.
What are the products of light-dependent reactions?
The products of light-dependent reactions are ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), both of which serve as energy carriers.
Where does the light-independent reaction occur?
The light-independent reaction, also known as the dark reaction or the Calvin cycle, occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts.
Definition of Light Reaction?
The initial stage of photosynthesis occurs in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, capturing light energy to produce ATP, NADPH, and oxygen gas.
Definition of Dark Reaction?
The second stage of photosynthesis, also known as the Calvin Cycle, taking place in the stroma of chloroplasts to use ATP and NADPH produced in the light reaction to fix carbon dioxide and create glucose.
