What is Nephron? – Structure, Functions, Types

The nephron is a vital component of the human kidney responsible for its primary function, urine formation. It acts as a microscopic filtration unit, efficiently removing waste products and regulating fluid balance in the body. In this article, we shall explore the structure of the nephron, its functions, and types and parts of nephrons, in detail to gain a comprehensive understanding of their significance. It is important to understand the parts and analyze the structure and functions of a nephron, to understand the human kidney better.
Introduction
The human kidney is a remarkable organ that performs various functions essential for maintaining overall health. The nephron is the fundamental structural and functional unit of the kidney, responsible for the filtration and purification of blood. It is the core of the kidney that determines the state and strength of the kidneys. The structure and function of nephrons invariably decide the overall functioning of the human kidney. A careful observation of the nephron diagram in the later section of this blog post will help you gain more insights with the help of the illustration.
What is Nephron?
There are at least one million nephrons in each kidney, and together, they drive the kidneys, collectively serving as the functional unit responsible for filtering blood and regulating the body’s fluid balance. As we explore the structure and functions of nephrons and parts of nephrons, we shed light on their significance in maintaining overall health.
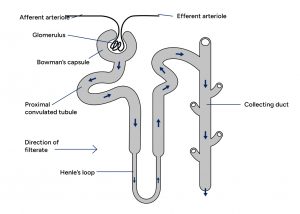
Nephron Diagram
The Diagram for Nephron is shown below,
Importance in Kidney Function
As you may observe in the Nephron diagram, these play a crucial role in maintaining the body’s fluid balance, regulating blood pressure, and eliminating waste products. They work in harmony with blood vessels and other components of the kidney to ensure proper filtration and excretion of metabolic waste.
Structure of Nephron
There are two kinds of nephrons, superficial cortical nephrons that comprise 70-80%, and the rest being juxtamedullary nephrons. A look at the parts structure of nephrons, we realize that they consist of two primary components: the renal corpuscle and the renal tubule.
Renal Corpuscle
Among the parts of a nephron, the renal corpuscle is a key one and also the initial site of blood filtration. It spearheads the core function nephron, through the glomerulus, a network of tiny blood vessels, and the Bowman’s capsule, which surrounds the glomerulus. The glomerulus acts as a sieve, allowing small molecules such as water, electrolytes, and waste products to pass through while preventing the passage of larger molecules such as proteins and blood cells.
Renal Tubule
The next among the major parts of a nephron is the renal tubule, a long, convoluted structure that continues from the Bowman’s capsule. It consists of several segments, each with specific functions. These segments include the proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, and collecting duct.
Functions of Nephron
The Nephron functions are explained below,
Filtration
Filtration is the first step in urine formation and occurs in the renal corpuscle. As blood passes through the glomerulus, the high pressure forces water, ions, nutrients, and waste products out of the blood and into the Bowman’s capsule. This fluid, known as the filtrate, contains substances that need to be selectively reabsorbed or excreted.
Reabsorption
Reabsorption takes place primarily in the renal tubule. Essential substances, such as glucose, amino acids, and water, are selectively reabsorbed into the surrounding capillaries to be returned to the bloodstream. This process ensures that vital molecules are retained in the body, maintaining balance.
Secretion
Secretion involves the transfer of additional substances, such as excess ions, drugs, and toxins, from the blood into the renal tubule. This process allows the nephron to regulate the concentration of certain substances in the body, aiding in the elimination of waste and maintenance of homeostasis.
Excretion
Excretion is the final step in urine formation. After the filtrate has undergone reabsorption and secretion processes in the renal tubule, it reaches the collecting duct. Here, additional water and solutes are reabsorbed or excreted based on the body’s needs, resulting in the formation of concentrated urine.
Types of Nephrons
There are two main types of nephrons: cortical nephrons and juxtamedullary nephrons.
Cortical Nephrons
Cortical nephrons are the most abundant type, comprising approximately 85% of all nephrons. They are primarily located in the outer region of the kidney cortex and have a shorter loop of Henle. These nephrons are involved in maintaining overall body fluid balance.
Juxtamedullary Nephrons
Juxtamedullary nephrons are located closer to the medulla of the kidney and have a longer loop of Henle. They play a crucial role in producing concentrated urine and are involved in the body’s water conservation mechanisms.
Conclusion
The nephron, as the functional unit of the kidney, performs vital tasks to maintain fluid balance, regulate blood pressure, and eliminate waste products from the body. It is an intricate system that ensures the proper filtration, reabsorption, and secretion processes required for overall health and well-being.
Understanding the structure and functions of nephrons, and their types provides valuable insights into the complex processes involved in urine formation. The nephron’s remarkable capabilities enable the body to maintain a delicate balance and eliminate waste effectively. By comprehending the significance of nephrons, we can appreciate the intricacies of the human body’s filtration system.
Hope our article has introduced you to more interesting information about the human body, and added extra knowledge. Tutoroot, as an educational institute offers online tuition classes with a personalised touch. Click here to book a Free demo of our live interactive sessions for NEET Online Tuitions and much more for the various boards.
FAQs
Which ion is both secreted and absorbed by the nephron?
The ion that is both secreted and absorbed by the nephron is potassium (K+). It is important for maintaining proper electrolyte balance in the body, and its levels are tightly regulated by the nephron.
Which part of the nephron is impermeable to water?
The ascending limb of the loop of Henle is impermeable to water. This section of the nephron plays a crucial role in establishing the concentration gradient necessary for water reabsorption in the collecting duct.

this site is good i appriciat it
That’s was wonderful en thanks