What is Plant Cell and Animal Cell? – Definition, Diagrams, Difference
Plant and Animal cells, both alike, play a major role in the evolution of respective species, and thus it will be important for the students to understand the differences between Plant cells and Animal cells, and their various functions, features as well as their components. Therefore, to help you out, we have decided to provide a detailed guide about both plant cells and animal cells and their differences, here in the article below.
What is a Plant Cell?
A Plant cell is defined as a eukaryotic cell, which consists of various components such as a nucleus and multiple organelles, each performing different types of functions. This is why these cells are stated as fundamental blocks of plant life, as they perform important functions, such as Photosynthesis, which involves the conversion of carbon dioxide into food or starch. There are different types of plant cells, which we are going to explain briefly in the below section.
The plant cells are rectangular in shape with the presence of mitochondria in a limited number where the mode of nutrition is primarily autotrophic. These plant cells are organelles that can be larger in size compared to animal cells
- Collenchyma Cells – This cell is made up of elongated living cells, with irregular thick walls, which perform various functions, such as providing support, mechanical strength, and flexibility to the plants.
- Xylem Cells – These types of cells play an important role in the transfer of water as well as dissolved chemicals and minerals through various parts of the plant. Examples of Xylem Cells are Tracheids, Xylem Parenchyma, Xylem Fibers, etc.
- Sclerenchyma Cells – The cells that do not see any development, even though they are primary sustaining cells, these types of cells are called Sclerenchyma cells. Moreover, these cells are stiffer in nature and are generally dead cells as they mature.
- Phloem Cells – In order to transfer carbohydrates, sugar, amino acids, and nutrients, which are dissolved in water, the Phloem cells play an important role.
- Parenchlyma Cells – Most plants are made up of these cells, such as plant tissues, leaves, plant organs, and many more. The main function of these cells is to safely store proteins and carbohydrates, and also help the plants heal.
What is an Animal Cell?
This is a type of eukaryotic cell that does not contain a cell wall, instead has a true membrane-bound nucleus, that has multiple cellular organelles. However, unlike plant cells, these types of cells do not have the ability to produce their own nutrition. Besides this, there are three main components of the Animal Cells such as cytoplasm, nucleus, and cell membrane. Similar to Plant Cells, there are multiple types of animal cells, like,
The animal cells are irregular in shape or often found in round shape too. They are usually smaller than plant cells. As far as mitochondria in animal cells are concerned, they are found in large quantities. The nutrition mode for animal cells is heterotrophic. The normal range of an animal cell can be between 10-30 micrometers, as compared to the plant cell range which can be between 10 and 100 micrometers.
The typical composition of animal cells is more or less similar to that of a plant cell, which includes organelles that are membrane-bound, like endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, lysosomes, the nucleus, and Golgi apparatus.
- Skin Cells – As the name itself suggests, these cells are commonly found in epidermal and dermal layers of skin, which play an active role in acting as a barrier, and also preventing water loss.
- Nerve Cells – As you know already, these are one of the most important cells in an animal body, as their function is to transmit information or impulses. And through these impulses, send and receive messages.
- Bone Cells – For the improvement or formation of an animal’s skeleton and bones, these cells communicate with each other in order to maintain the structure and density of bones throughout the animal skeleton.
- Muscle Cells – In order to organize the movement of limbs and various organs, muscles are required. Furthermore, it also helps in protecting the delicate organs of the animal body.
- Blood Cells – The main function of these cells is to transport oxygen, nutrients, and hormones throughout the body, through the bloodstream.
Diagrams of Plant Cell and Animal Cell
The diagrams of plant cell and animal cell are schematic below,
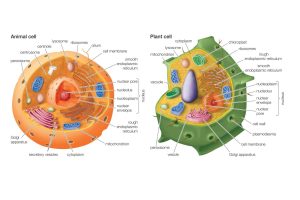
Distinguish Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell
There are many differences between Plant Cell and Animal Cell Diagram, such as,
| Parameters | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
| Type of Nucleus | True Nucleus | Membrane Bound-Nucleus |
| Size & Shape | Fixed Size type of plant cell, that is larger in size. | Irregular type cell, that is very small in size. |
| Cell Wall | It consists of cell walls made up of cellulose and membrane. | It does not have any cell walls. |
| Plastids | Plastids are present in this type of cell. | Plastids are generally absent. |
| Lysosomes | Present, but are generally rare. | Present, but are abundant. |
| Size of Vacuole | Vacuoles are large in size. | Vacuoles are very small in size. |
| Chloroplast | Present. | Not Absent. |
| Location of Nucleus | On one side of a cell. | Lies in the center of the cell. |
Conclusion
From the above article, you can clearly understand the difference between plant and animal cells, as well as their components and various important functions. And now that you have covered it, if you have any doubts about any other topics or chapters in this subject, then it would be a good idea for you to join an online coaching class. Moreover, currently, the Tutoroot platform is offering cost-effective online interactive classes, with various amazing features. If you are interested, please visit the official website to learn more.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between a plant and an animal cell?
The main difference between plant cells and animal cells is that only plant cells have plastids and cell walls.
Few Differences Between Plant cell and Animal Cell
As far as the differences between plant cells and animal cells are concerned, there are multiple aspects that show the variations. Beginning from size, shape, and nucleus, chloroplasts, location of the nucleus, and aspects related to the cell walls and plastics, plant cells, and animal cells differ in many ways.
However, the main difference between plant cells and animal cells is that only plant cells have plastids and cell walls, which is it not the case in animal cells.
A detailed analysis of the difference between plant cells and animal cells can be summarized like this:
As far as the Nucleus type in plant cells is concerned, it is the true nucleus, while it is a membrane-bound nucleus in animal cells. Fixed-size type of plant cell is apparent, that is larger in size, while it is irregular type cell, that is very small in size when it comes to animal cells.
The cell walls in plant cells are made up of cellulose and membrane, whereas animal cells do not have cell walls. Plastids are present in plant cells but are absent in animal cells.
Lysosomes are present in plant cells but are rare while they are abundant in animal cells. For plant cells, vacuoles are large in size, whereas in animal cells, they are very small in size. Plant cells have chloroplast but the same is not the case in animal cells. Another major difference between plant cells and animal cells is the location of the nucleus. In the case of plant cells, it is located on one side of the cell, whereas it lies in the center of the animal cell.
