What are Ecological Pyramids? – Definition, Types, Importance
What is Ecological Pyramid?
A graphical depiction of the relation between various living species at different trophic levels is an ecological pyramid. The pyramid of numbers was invented by Charles Elton. Later, G.Evylen Hutchinson and Raymond Lindeman proposed the energy or production pyramid.
These pyramids have the form of genuine pyramids, with the base being the broadest and being covered by the lowest trophic level, i.e., producers. The next trophic level, i.e., the primary consumers, occupies the next level, and so on.
All calculations for the creation of these sorts of ecological pyramids must take all the organisms into consideration at a certain trophic level since a sample space of a few numbers or a few species will result in a high degree of inaccuracy.
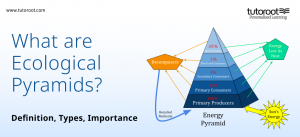
Importance of Ecological Pyramids
- An ecological pyramid demonstrates how effectively energy is transported from one level to the next and aids in the quantification of energy in a food chain.
- This pyramid also demonstrates how different creatures in different ecosystems feed on one another, highlights their dietary patterns, and illustrates the relationship between the many layers inside it.
- The ecological pyramid also aids in monitoring an ecosystem’s general health and condition, as well as in the restoration of equilibrium. It also aids in understanding how additional harm to an environment might be avoided.
Types of Ecological Pyramids
There are three types of ecological pyramids.
Pyramids of Number
The number of creatures in each trophic level is considered a level in this form of ecological pyramid. Except in rare cases, such as the detritus food chain, where numerous creatures feed on a single dead plant or animal, the number pyramid is normally vertical.
Pyramid of Biomass
The total mass of living creatures in a population present at a given moment and location is represented by biomass. The biomass pyramid illustrates the biomass of an ecosystem’s different trophic levels, grouped in the shape of a pyramid, with the lowest trophic level at the bottom and rising further up. Except in extreme circumstances, the pyramid is upright, such as in the ocean, where the quantity of phytoplanktons is fewer than the number of zooplanktons that rely on them.
Pyramid of Energy
The energy pyramid is the only form of an ecological pyramid that is always upright since energy transfer in a food chain is always unidirectional. In addition, when trophic levels rise, some energy is wasted in the environment.
Limitations of Ecological Pyramids
- The ecological pyramid ignores saprophytes and regards them as inconsequential in the ecosystem, even though they play a critical role in maintaining environmental equilibrium.
- This pyramid makes no mention of diurnal or seasonal fluctuations; the idea of climate or seasons is totally absent.
- The ecological pyramid is only valid in the scenario of simple food chains, which are uncommon in and of themselves.
- The ecological pyramid also does not explain the notion of a food chain.
- This pyramid makes no mention of the rate of energy transfer from one trophic level to the next.
- Important sources of energy, such as trash and humus, are largely neglected in the ecological pyramid, despite their immense value in the ecosystem.
- The presence of the same species at different levels of a pyramid is not considered.
Final Notes
To know more about ecological pyramids and other topics in Biology, enroll in Tutoroot’s Biology classes. Our experienced faculty will help you improve your grades with exclusive personalized one on one classes.
FAQ’s
How many types of ecological pyramids are there?
Three types of ecological pyramids.
- Pyramid of numbers
- Pyramid of biomass
- Pyramid of energy
What are the trophic levels and ecological pyramids?
Trophic Level: The place of an organism in the food chain.
Ecological Pyramid: a graphical depiction of a specific ecosystem’s biomass at each trophic level.
