What is Cannizzaro Reaction? – Cannizzaro Reaction Mechanism
Introduction to the Cannizzaro Reaction
The Cannizzaro Reaction is a chemical process discovered by Italian chemist Stanislao Cannizzaro in 1853. This unique reaction involves the conversion of an aldehyde into a corresponding alcohol and carboxylic acid, making it a significant transformation in organic chemistry. Understanding the intricacies of the Cannizzaro Reaction opens a world of possibilities in chemical synthesis.
What is Cannizzaro Reaction?
The Cannizzaro Reaction is a type of redox reaction between two molecules of an aldehyde without a suitable hydrogen acceptor. Unlike most reactions involving aldehydes, where one molecule acts as a reducing agent and the other as an oxidizing agent, in Cannizzaro Reaction, both molecules transform. This reaction is an essential part of organic chemistry, providing insights into the behavior of aldehydes.
What is Cannizzaro Reaction Reagent?
To kickstart the Cannizzaro Reaction, a strong base such as hydroxide or carbonate is typically used as the reagent. This reagent plays a key role in facilitating the cleavage of the aldehyde and directing the products towards alcohol and carboxylic acid formation.
Exploring the Cannizzaro Reaction Chemical Equation
The Cannizzaro Reaction chemical equation showcases the transformation of an aldehyde into an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. It is represented by the following equation:
[2 RCHO → RCOH + RCO2H]
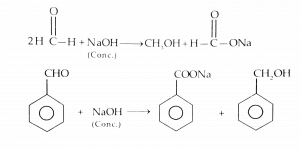
Illuminating Cannizzaro Reaction Examples
To better grasp the concept of the Cannizzaro Reaction, An example of the Cannizzaro Reaction is the oxidation of benzaldehyde. When benzaldehyde undergoes the Cannizzaro Reaction, it forms benzoic acid and benzyl alcohol. This reaction can be represented as:
2 C6H5CHO → C6H5COOH + C6H5CH2OH
Unveiling the Complete Cannizzaro Reaction Mechanism
The complete mechanism of the Cannizzaro Reaction involves a series of steps, including nucleophilic attack, hydride transfer, and proton transfer. These intricate steps showcase the complexity and beauty of this chemical transformation.
Now, let’s peek behind the curtain to understand the magic – the Cannizzaro Reaction Mechanism. Imagine our benzaldehyde dancers under the spotlight. The hydroxide ion, like a dance instructor, guides the reaction. It grabs one molecule, steals hydrogen, and leaves it with a negative charge. Meanwhile, the other molecule receives the stolen hydrogen, turning it into alcohol, while the first becomes an acid. The solvent plays a crucial role, in influencing the entire dance routine.
Let’s take a closer look at this mechanism using a real-life scenario: the transformation of benzaldehyde into benzyl alcohol and benzoic acid.
- Initiation: The hydroxide ion (OH-) grabs hydrogen from one benzaldehyde molecule, leaving it with a negative charge.
- Hydride Transfer: The negatively charged benzaldehyde now steals a hydride ion (H-) from another benzaldehyde molecule. This transforms the first benzaldehyde into benzoic acid and the second into benzyl alcohol.
- Completion: The dance concludes, leaving us with benzyl alcohol and benzoic acid as the final products.
This detailed breakdown helps us understand how the Cannizzaro Reaction unfolds, transforming aldehydes into alcohol and acids.
What is the Cross-Cannizzaro Reaction?
In a Cross Cannizzaro Reaction, two different aldehydes react with each other in the presence of a strong base. One aldehyde undergoes oxidation to form the corresponding carboxylic acid, while the other aldehyde is reduced to the corresponding alcohol. This reaction is particularly useful in organic synthesis for generating a mixture of alcohol and carboxylic acid from two different aldehydes.
Practical Applications and Uses of the Cannizzaro Reaction
The Cannizzaro Reaction finds wide applications in organic synthesis, particularly in the preparation of various alcohol and carboxylic acid derivatives. From pharmaceuticals to fine chemicals, the versatility of the Cannizzaro Reaction makes it a valuable tool in the hands of chemists.
Here are a few uses of the Cannizzaro reaction,
- Chemical Synthesis: It is utilized in the synthesis of specific alcohols and carboxylic acids.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: It plays a crucial role in the synthesis of certain pharmaceutical compounds.
- Organic Chemistry Research: Chemists employ the Cannizzaro Reaction to understand reaction mechanisms and develop new synthetic routes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Cannizzaro Reaction stands as a cornerstone in organic chemistry, offering a pathway to transform aldehydes into useful alcohol and carboxylic acid compounds. By understanding its mechanisms, examples, and applications, we can appreciate the beauty and utility of this fundamental chemical process. So, let’s continue exploring the wonders of the Cannizzaro Reaction and unlock its full potential in the world of chemistry.
Remember, the key to successful incorporation of the Cannizzaro Reaction in your chemical repertoire lies in understanding its nuances and applications. So, keep experimenting, learning, and discovering new possibilities with this fascinating chemical transformation. Let the Cannizzaro Reaction guide you on your journey towards chemical innovation!
Are you looking to effortlessly understand complex concepts? Explore our TutorEase Blog for simplified explanations and insights. Elevate your comprehension of various subjects and get your doubts resolved through Tutoroot’s interactive online tutoring. Embark on a journey of effective learning with TutorEase’s online home tuitions – sign up now for a complimentary FREE DEMO session.
FAQs
What is Cannizzaro’s reaction with example?
The Cannizzaro Reaction involves the oxidation and reduction of an aldehyde to give a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. An example of this reaction is the conversion of benzaldehyde to benzoic acid and benzyl alcohol.
What is aldol and Cannizzaro reaction?
The aldol reaction involves the formation of a beta-hydroxy aldehyde or beta-hydroxyketone from the condensation of an aldehyde or ketone with an enolate ion. However, the Cannizzaro Reaction involves the oxidation and reduction of an aldehyde to yield a carboxylic acid and alcohol.
