What are the Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Mixtures?
While learning Chemistry, students come across mixtures that contain the combination of one or more elements or substances which is important for the understanding of these mixtures, and to find out their various parameters such as melting and boiling points. Students must have a good understanding of Heterogeneous mixtures and Homogeneous mixtures, and their differences, while also being able to list examples. In this article, let us learn more about
- Heterogeneous Mixture and Homogenous Mixture
- Properties of Heterogenous Mixture
- Properties of Homogeneous Mixture
- Examples of Homogeneous Mixture
- Examples of Heterogeneous Mixture
Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Mixtures
Firstly, what is a mixture?
In chemistry, a mixture is defined as a substance that is formed out of two or more substances that are not chemically combined but physically blended. This infers that there is an absence of any kind of chemical bonds between these different and distinct substances, either in a homogeneous mixture or heterogeneous mixture.
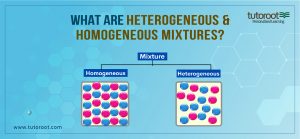
What is a Heterogeneous Mixture?
A heterogeneous Mixture is defined as the type of mixture where there is no uniformity, as different types of components are mixed in it. However, unlike other mixtures, the components in the Heterogeneous mixture can be observed or detected quickly, thus making it easier to separate the components because of no uniformity. Some of the popular examples of Heterogeneous Mixtures are Suspensions and Colloids, as well as Soil.
Properties of Heterogenous mixtures
The heterogeneous mixtures properties are given below,
- In the case of heterogeneous mixtures, there is no uniform distribution of particles that becomes its core property.
- Another of the most important properties of heterogenous mixtures is that they are visible.
- The most important of the properties of heterogenous mixtures is that they cannot be chemically bonded
Examples of Heterogenous mixtures
Let’s discuss the examples of homogeneous mixtures, here we have listed a few homogeneous mixtures examples.
- Saltwater: A classic example, where salt (solute) dissolves in water (solvent) to create a homogeneous mixture, commonly found in our oceans and even in our kitchens.
- Air: The air we breathe is a mixture of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and more. Despite their differences, these gases blend uniformly in the atmosphere.
- Sugar in Coffee: When you stir sugar into your morning coffee, it dissolves uniformly, forming a homogeneous mixture that sweetens your beverage.
- Vinegar: A mixture of acetic acid and water, vinegar is commonly used in cooking and cleaning.
- Alloyed Metals: Brass, bronze, and steel are examples of homogeneous mixtures of different metals. These alloys combine distinct metals to create materials with desirable properties.
- Fruit Juice: Fruit juices are homogeneous mixtures composed of water, sugars, vitamins, and other compounds that give them their unique flavours.
Understanding these examples of homogeneous mixtures is vital in various scientific, industrial, and culinary applications. Whether it’s cooking, manufacturing, or environmental science, the knowledge of homogeneous mixtures plays a crucial role in our daily lives.
What is a Homogeneous Mixture?
Another type of mixture, where the components are uniformly distributed, is referred to as the Homogeneous Mixture. Moreover, the mixture cannot be generally observed or detected as the components cannot be identified or separated because of the uniformity. Thus, in reality, the components in the mixture, have different compositions. Alloys and Solutions are some of the common examples of the Homogeneous Mixture.
Properties of homogeneous mixtures
The main properties of the homogeneous mixture have been listed below,
- In the case of homogenous mixtures, the following properties are apparent
- Homogenous mixtures look uniform visually and are completely transparent even in case of being coloured
- Homogenous mixtures consist of a single phase and don’t undergo changes when they are put through filters or pass through porous membranes
Examples of Homogeneous mixture
The examples of homogenous mixtures are given below along with some information for better understanding.
- Saltwater: A classic example, salt dissolves uniformly in water, resulting in a homogeneous mixture. This mixture is abundant in our oceans, as well as in the salt shakers on our dining tables.
- Air: The air we breathe is a homogeneous mixture of various gases, including nitrogen, oxygen, and argon. Despite their different properties, these gases are uniformly distributed in the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Soda: Carbonated beverages like soda are homogeneous mixtures of carbon dioxide gas, water, sugar, and flavourings. The even distribution of these components gives soda its refreshing taste.
- Mouthwash: Many types of mouthwash are homogeneous mixtures containing water, alcohol, and various antiseptic and flavouring agents. This uniform blend helps maintain oral hygiene.
- Vinegar: A mixture of acetic acid and water, vinegar is a commonly used homogeneous solution in cooking and cleaning.
- Liquid Soaps: Liquid hand soaps are homogeneous mixtures of water, surfactants, fragrances, and other additives. These components are uniformly mixed, providing effective cleansing properties.
Understanding these examples of homogeneous mixtures is not only essential for scientific knowledge but also for various practical applications in industries such as food, healthcare, and manufacturing. These mixtures exemplify the importance of uniform composition in our daily routines.
Characteristics of Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Mixtures
As we understand, all mixtures, heterogeneous mixture or homogenous mixture, are naturally composed of two or more pure substances. These can be elements or compounds. Let us primarily spot the difference between a mixture and a compound and how exactly these substances combine to form them. Compounds are seen as pure substances since they possess only molecule types. Molecules as we know are made of atoms that bond together. In the case of a mixture, these elements are mixed physically but not chemically, meaning there is strictly no atomic bonds formed form between the constituent substances.
Both heterogenous mixture and homogenous mixture can be cohesive. In the case of a homogeneous mixture, it is referred to as a solution in which substances mix so perfectly that individual differentiation cannot be spotted or sensed. The composition stays is uniform because the constituents in a homogeneous mixture happen in the same proportion concerning every section of the mixture.
On the contrary, in the case of a heterogeneous mixture, the constituent substances are not distributed uniformly and visually the difference is clear. The separation in the case of a heterogenous mixture is easier, while homogeneous mixtures too can be separated.
Differences between Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Mixtures
There are multiple differences between Homogeneous and Heterogeneous mixtures, which we are going to explain briefly here in this section. Differences such as,
| Parameters | Heterogeneous Mixture | Homogeneous Mixture |
| Definition | A mixture is made of different types of components and is not uniform. | This type of mixture is observed when the different components have a uniform composition. |
| Visibility | These mixtures can be easily viewed through the naked eye. | Whereas the Homogeneous mixture cannot be observed or detected through the naked eye. |
| Particle Size | The size of the particles in this mixture is very large. | However, inhomogeneous mixture, the particle size is limited to the molecular or atomic level. |
| Physical Properties | All the components in the Heterogeneous mixture have different physical properties. | All the components in a Homogeneous mixture have similar physical properties. |
| Examples | Stone pieces, salt and water mixture, grains, pulses, etc. | Air, salt, and sugar solution.
|
Conclusion
The above article provided a detailed guide to Heterogeneous and Homogeneous mixtures, their differences, and examples. If you are facing trouble studying any other topics in Chemistry subject, then you can join the Online Interactive Classes offered by the Tutoroot platform. Through these courses, the students can access various benefits such as Exclusive Doubt Sessions, Customizable Time Tables, Access to Best Educational Material, Top Staff Guidance, and many more.
For more simplified explanations like the one above, visit the chemistry blogs on the Tutoroot website. Elevate your learning with Tutoroot’s personalised Chemistry online tuition. Begin your journey with a FREE DEMO session and discover the advantages of one on one online personalised tuitions.
FAQs
What is a Heterogeneous Mixture?
A heterogeneous Mixture is defined as the type of mixture where there is no uniformity, as different types of components are mixed in it. However, unlike other mixtures, the components in the Heterogeneous mixture can be observed or detected quickly, thus making it easier to separate the components because of no uniformity. Some of the popular examples of Heterogeneous Mixtures are Suspensions and Colloids, as well as Soil.
What is a Homogeneous Mixture for example?
Another type of mixture, where the components are uniformly distributed, is referred to as the Homogeneous Mixture. Moreover, the mixture cannot be generally observed or detected as the components cannot be identified or separated because of the uniformity. Thus, in reality, the components in the mixture, have different compositions. Alloys and Solutions are some of the common examples of the Homogeneous Mixture.
Examples of Homogeneous Mixture
Certain known examples of a homogenous mixture
- Saltwater
- Milk
- Air
- Sodas
- Cement
- Gum and glues
- Certain Alloys
Examples of Heterogeneous Mixture
Certain common examples of heterogenous mixtures are:
- Sand
- Salads and soups
- Oils
- Granite and concrete
- Open Sodas
Is Milk a Homogeneous Mixture?
Yes, milk is an example of a homogenous mixture
What are the properties of Heterogenous Mixtures?
In the case of heterogeneous mixtures, there is no uniform distribution of particles that becomes its core property. Among the important properties of heterogenous mixtures is that they are visible. The most important among the properties of heterogenous mixtures is that they cannot be chemically bonded.
What are the properties of Homogeneous Mixtures?
In the case of homogenous mixtures, the following properties are apparent
Homogenous mixtures look uniform visually and are completely transparent even in the case of being coloured. Homogenous mixtures don’t undergo changes when they are put through filters or pass through porous membranes.
